Bourgeanic acid
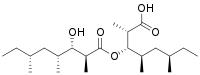
Bourgeanic acid is a fatty acid with the molecular formula C22H42O5.[2][3][1] Bourgeanic acid is a lichen metabolite.[3][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4R,6R)-3-[(2S,3S,4R,6R)-3-hydroxy-2,4,6-trimethyloctanoyl]oxy-2,4,6-trimethyloctanoic acid[1] | |
| Other names
(+)-bourgeanic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H42O5 | |
| Molar mass | 386.573 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "Bourgeanic acid". Pubchem.ncbi.NLM.nih.gov.
- Brodo, Irwin M.; Sharnoff, Sylvia Duran; Sharnoff, Stephen; Nature, Canadian Museum of (1 January 2001). Lichens of North America. Yale University Press. p. 247. ISBN 978-0-300-08249-4.
- Majumdar, Krishna C.; Chattopadhyay, Shital K. (15 June 2011). Heterocycles in Natural Product Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. p. 32. ISBN 978-3-527-63489-7.
Further reading
- Johnson, Alan Thomas (1990). Total Synthesis of (+)-bourgeanic Acid and Conformational Analysis of Its Dilactone. Oregon State University.
- Yadav, Jhillu; Rao, Tenneti; Yadav, Nagendra; Rao, Kovvuru; Reddy, Basi; Al Khazim Al Ghamdi, Ahmad (March 2012). "Chemoenzymatic Approach to the Total Synthesis of (+)-Bourgeanic Acid". Synthesis. 44 (5): 788–792. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1289699.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.