Bouvardin
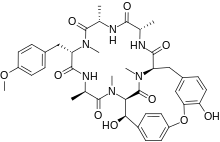
Bouvardin is a bicyclic hexapeptide isolated from Bouvardia ternifolia. Its chemical formula is C40H48N6O10. It is derived from the amino acid sequence Ala-Ala-Tyr-Ala-Tyr-Tyr. It has demonstrated certain anti-cancerous activities by inhibiting protein synthesis through inhibition of 80S ribosomes (eukaryotic ribosomes).[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1S,4R,7S,10S,13S,16S,17S)-17,24-Dihydroxy-10-(4-methoxybenzyl)-4,7,9,13,15,29-hexamethyl-22-oxa-3,6,9,12,15,29-hexaazatetracyclo[14.12.2.218,21.123,27]tritriaconta-18,20,23(31),24,26,32-hexaene-2,5,8,11,14,30-hexone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C40H48N6O10 | |
| Molar mass | 772.8 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
The synthetic derivative of bouvardin SVC112 suppresses cancer stem cells and inhibits growth in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.[2]
References
- Boger, Dale L; Patane, Michael A; Zhou, Jiacheng (1994). "Total Synthesis of Bouvardin, O-Methylbouvardin, and O-Methyl-N9-desmethylbouvardin". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 116 (19): 8544–8556. doi:10.1021/ja00098a015.
- Keysar, Stephen B (2020). "Inhibiting translation elongation with SVC112 suppresses cancer stem cells and inhibits growth in head and neck squamous carcinoma". Cancer Research. 80 (5): 1183–1198. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3232. PMC 7056512. PMID 31911553.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.