Bréguet 410
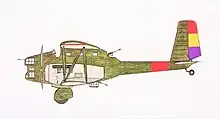
The Bréguet 410 was a French bomber of the early 1930s. Not many of these twin-engined sesquiwing biplanes were built. At least one Breguet 413, one of its variants, was sold to the Spanish Republican Air Force during the Spanish Civil War.[1]
| Bréguet 410 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Bomber aircraft |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Bréguet |
| First flight | 1931 |
| Variants | Breguet 460 |
Design and development
The Bréguet 410 was a sesquiplane prototype designed by Breguet Aviation in order to meet the requirements of the Technical Aeronautic Service ( Service Technique de L'Aéronautique ) of the French government towards the end of the 1920s, for a bomber and reconnaissance plane type designated as Multiplace de Combat.[2] It had a steel frame covered with duralumin; its armament was two front and two rear 7.7 mm Lewis machine guns and it could carry a bombload up to 1300 kg.[3]
Only one unit of the first variant, the Bréguet 410, was built, which was passed in favour of the competing Amiot 143 despite its combat qualities. Other prototypes, such as the Blériot 137 and the SPCA 30, underwent a similar fate as the Bréguet 410.[4] Most of its later developments or variants never went past the prototype stage.
Operational history
The sole Bréguet 410 flew in 1931 powered by two Hispano-Suiza 12Nb engines. Developments followed though, with an upgraded and slightly modified version, the Bréguet 411, which flew in 1932. Like its predecessor this Bréguet aircraft was again rejected by the French government.[5]
The Bréguet 413 was an improved version, fitted with more powerful Hispano-Suiza 12Ybrs engines. Four units were constructed for the Armée de l'Air, the first one of which flew in February 1933.[6] At least one of these became part of the Escadrille Internationale and was sent to the Spanish Republican Air Force at the beginning of the Civil War in that country, but its fate is unknown.[1]
A further development followed, the Bréguet 414, fitted with Gnome-Rhône 14Kdrs engines and first flew in November 1933. The sole 414 crashed in 1940.[7]
The improved Bre 420 first flew on 13 August 1936, but failed to improve performance and handling enough to warrant production.[8]
Variants
- Bre 410 M4
- Light bomber with two HS12Nb engines (1931)
- Bre 411 M5
- Light bomber with two HS12Nb engines, (1932 - one built).[9]
- Bre 413
- Bre 413 M4
- Light bomber with two HS12Ybrs engines[6]
- Bre 414
- Light bomber with two GR14Kirs radial engines (1933).
- Bre 420
- An improved 414 with modified rear fuselage and tail section.[11]
Operators
Specifications
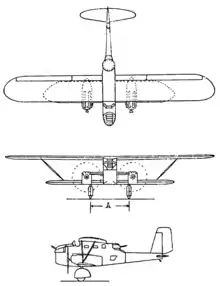
Data from [6]
General characteristics
- Crew: four
- Length: 11.30 m (37 ft 1 in)
- Wingspan: 20.20 m (66 ft 3 in)
- Height: 5.09 m (16 ft 8 in)
- Wing area: 67.15 m2 (722.8 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 3,500 kg (7,716 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 7,200 kg (15,873 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Hispano-Suiza 12Y 36-litre water-cooled V12 engine, 480 kW (650 hp) 650 cv each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 310 km/h (190 mph, 170 kn)
- Cruise speed: 285 km/h (177 mph, 154 kn)
- Range: 1,300 km (810 mi, 700 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 10,000 m (33,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 7.24 m/s (1,425 ft/min)
Armament
- Guns: 4 × 7.7 mm Lewis machine guns (2 forward, 2 rearward)
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
References
- Boeing Bellanca y otros (in Spanish)
- William Green, War planes of the Second World War: Volume 7
- Bréguet Bre 410 (in French)
- SPCA 30
- Airwar - Breguet 410
- Airwar - Breguet 413
- Airwar - Breguet 414
- Airwar - Breguet 420
- SP - Avions Bréguet (Br) designations
- Bre 413
- Bre 414
Bibliography
- Cortet, Pierre (August 2000). "Les bimoteurs à "poutre" Breguet 41" [The Beamy Twin-engined Breguet 41]. Avions: Toute l'Aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (89): 44–50. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Cortet, Pierre (October 2000). "Courrier des Lecteurs" [Readers' Letters]. Avions: Toute l'Aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (91): 3–4. ISSN 1243-8650.
- Cortet, Pierre (February 2000). "Rétros du Mois" [Retros of the Month]. Avions: Toute l'aéronautique et son histoire (in French) (83): 5. ISSN 1243-8650.