Lake Brienz
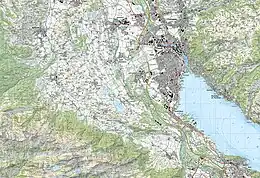
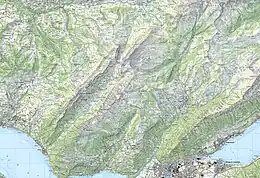
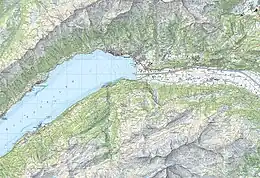
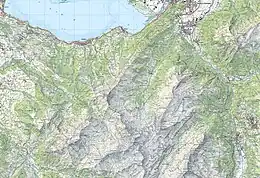
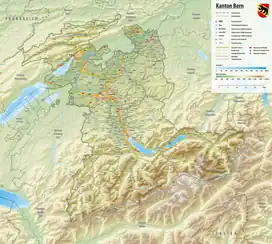
Lake Brienz (German: Brienzersee) is a lake just north of the Alps, in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It has a length of about 14 kilometres (8.7 mi), a width of 2.8 kilometres (1.7 mi) and a maximum depth of 260 metres (850 ft). Its area is 29.8 square kilometres (11.5 sq mi); the surface is 564 metres (1,850 ft) above the sea-level. It is fed, among others, by the upper reaches of the Aare at its eastern end, the Giessbach at its southern shore from steep, forested and rocky hills of the high Faulhorn and Schwarzhoren more than 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) above the lake, as well as by both headwaters of the Lütschine, the Schwarze Lütschine (Black Lütschine) flowing from Grindelwald, and the Weisse Lütschine (White Lütschine) from the Lauterbrunnen Valley, at its southwestern corner. Not far north from Lütschine's inflow, the lake drains into a further stretch of the Aare at its western end.[1][2] The culminating point of the lake's drainage basin is the Finsteraarhorn at 4,274 metres above sea level.[3]
| Lake Brienz | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) Aerial view of Lake Brienz from the southwest | |
 Lake Brienz  Lake Brienz  Lake Brienz | |
| Location | Bernese Highlands, canton of Bern |
| Coordinates | 46°43′N 7°58′E |
| Native name | Brienzersee (German) |
| Primary inflows | Aare, Lütschine, Giessbach |
| Primary outflows | Aare |
| Catchment area | 1,127 km2 (435 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Switzerland |
| Max. length | 14 km (8.7 mi) |
| Max. width | 2.8 km (1.7 mi) |
| Surface area | 29.8 km2 (11.5 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 173 m (568 ft) |
| Max. depth | 260 m (850 ft) |
| Water volume | 5.17 km3 (4,190,000 acre⋅ft) |
| Residence time | 2.69 years |
| Surface elevation | 564 m (1,850 ft) |
| Islands | Schnäggeninseli (islet) |
| Settlements | Bönigen, Brienz, Iseltwald, Niederried, Oberried, Ringgenberg |
The village of Brienz, from which the lake takes its name, lies on the northern shore to its eastern end. In the west, the lake is terminated by the Bödeli, a tongue of land that separates it from neighbouring Lake Thun. The village of Bönigen occupies the lake frontage of the Bödeli, whilst the larger resort town of Interlaken lies on the reach of the Aare between the two lakes. The village of Iseltwald lies on the south shore, whilst the villages of Ringgenberg, Niederried and Oberried are on the north shore.[3][1][2]
The lake is poor in nutrients, and thus fishing is not very important. Nevertheless, in 2001 10,000 kg of fish were caught.
There have been passenger ships on the lake since 1839, and currently there are five passenger ships on the lake. The ships are operated by BLS AG, the local railway company, and link Interlaken Ost railway station, which they access using a 1.3-kilometre (0.81 mi) long navigable stretch of the Aare, with Brienz and other lakeside settlements. The ships also connect to the Giessbachbahn, a funicular which climbs up to the famous Giessbach Falls.[4][5]
The Brünig railway line follows the northern shore of the lake, along with a local road, whilst the A8 motorway adopts an alternative and mostly tunnelled route above the southern shore.[3]
References
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Coolidge, William Augustus Brevoort (1911). "Brienz, Lake of". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 4 (11th ed.). p. 562–563.
- "Lake Brienz". MySwitzerland.com. Switzerland Tourism. Retrieved 2013-01-03.
- "3 - Suisse sud-ouest" (Map). Brienzersee (2014 ed.). 1:200 000. National Map 1:200'000. Wabern, Switzerland: Federal Office of Topography – swisstopo. ISBN 978-3-302-00003-9. Retrieved 2017-12-11 – via map.geo.admin.ch.
- "History of navigation on Lakes Thun and Brienz". BLS AG. Archived from the original on 2009-11-15. Retrieved 2012-12-13.
- "BLS Schiffahrt - Our fleet". BLS AG. Archived from the original on 2016-08-10. Retrieved 2012-12-13.
External links
 Media related to Lake Brienz at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lake Brienz at Wikimedia Commons- Shipping pages from BLS AG web site
- Lake Brienz in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Ökosystem Brienzersee (in German) interdisciplinary study of the ecosystem
- Waterlevels at Ringgenberg from the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment