Buciclic acid
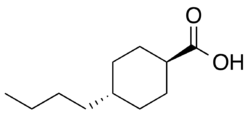
Buciclic acid, or bucyclic acid, systematic name trans-4-butylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, is a simple alkyl-substituted cyclohexanecarboxylic acid.[1] The salts and esters of buciclic acid are known as buciclates (bucyclates). Pharmaceutical examples of esters of this acid include testosterone buciclate, a long-acting prodrug of the androgen testosterone,[2] and dimethandrolone buciclate, a prodrug of dimethandrolone.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
trans-4-butylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Bucyclic acid, buciclate, bucyclate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.203.068 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H20O2 | |
| Molar mass | 184.279 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- "Essential Medicines and Health Products Information Portal" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on November 23, 2016.
- Shalender Bhasin (13 February 1996). Pharmacology, Biology, and Clinical Applications of Androgens: Current Status and Future Prospects. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 472–. ISBN 978-0-471-13320-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.