Bullia rhodostoma
Bullia rhodostoma, common name the smooth plough shell, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Nassariidae, the nassa mud snails or dog whelks.[1]
| Bullia rhodostoma | |
|---|---|
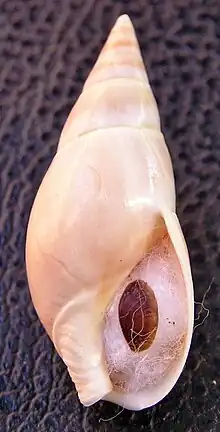 | |
| Apertural view of a shell of Bullia rhodostoma | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Subclass: | Caenogastropoda |
| Order: | Neogastropoda |
| Family: | Nassariidae |
| Genus: | Bullia |
| Species: | B. rhodostoma |
| Binomial name | |
| Bullia rhodostoma Reeve, 1847 | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Bullia (Bullia) rhodostoma Reeve, 1847 | |
Description
The length of the shell varies between 25 mm and 50 mm. Bullia rhodostoma are a slow growing, long-lived species with a life span of 15-20 years, following a 0.79 mortality rate, and 0.21 survival rate in their first 3 years. Successful adaptation has occurred because Bullia rhodostoma uses their single foot for crawling fast to search for food (usually stranded organisms, as they are carnivores), burying in the sand and surfing in the water on the shore. [2][3]
Distribution
This marine species occurs off South Africa.[3]
References
- Bullia rhodostoma. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 1 November 2012.
- Silva et al. 1987
- "Bullia rhodostoma". invasions.si.edu. Retrieved 28 September 2022.
Further reading
- Cernohorsky, Walter O. (1984). Systematics of the family Nassariidae (Mollusca: Gastropoda). Bulletin of the Auckland Institute and Museum. Vol. 14. OCLC 682230135. NAID 10016212571.
- Marais, J.P.; Kilburn, R.N. (2010). "Nassariidae". In Marais, Alwyn P; Seccombe, Alan D (eds.). Identification guide to the seashells of South Africa. Centre for Molluscan Studies. pp. 138–173. ISBN 978-0-620-48114-4. OCLC 843992336.
- Harris, Linda R.; Abrahams, Kelly; Bezuidenhout, Karien; Nel, Ronel (1 January 2017). "The relative role of intrinsic and extrinsic factors driving alongshore movement of swash-riding smooth plough shells, Bullia rhodostoma". Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 486: 77–86. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2016.09.009.
- Da Silva, F.M; Hodgson, A.N (January 1987). "Fine structure of the pedal muscle of the whelk Bullia rhodostoma reeve: Correlation with function". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology. 87 (1): 143–149. doi:10.1016/0300-9629(87)90437-3.
- Muteveri, T; Matthee, CA; Bowie, RCK; von der Heyden, S (2 January 2015). "High population connectivity and Pleistocene range expansion in the direct-developing plough shell Bullia rhodostoma along the South African coast". African Journal of Marine Science. 37 (1): 21–31. doi:10.2989/1814232X.2015.1010577. S2CID 85436924.
- McLachlan, A.; Cooper, C.; van der Horst, G. (January 1979). "Growth and Production of Bullia Rhodostoma on an Open Sandy Beach in Algoa Bay". South African Journal of Zoology. 14 (1): 49–53. doi:10.1080/02541858.1979.11447647.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bullia rhodostoma.
- Branch, G.M. et al. (2002). Two Oceans. 5th impression. David Philip, Cape Town & Johannesburg
- "Bullia rhodostoma". Gastropods.com. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.