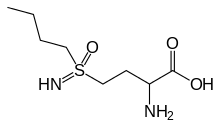
Buthionine sulfoximine
Buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) is a sulfoximine derivative which reduces levels of glutathione and is being investigated as an adjunct with chemotherapy in the treatment of cancer.[1] The compound inhibits gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase, the enzyme required in the first step of glutathione synthesis. Buthionine sulfoximine may also be used to increase the sensitivity of parasites to oxidative antiparasitic drugs.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-amino-4-(butylsulfonimidoyl)butanoic acid | |
| Other names
BSO | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.156.351 |
| MeSH | Buthionine+sulfoximine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H18N2O3S | |
| Molar mass | 222.305 g/mol |
| Density | 1.29 g/mL |
| Melting point | 215 °C (419 °F; 488 K) |
| Boiling point | 382.3 °C (720.1 °F; 655.5 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Defty, CL; Marsden, JR (2012). "Melphalan in regional chemotherapy for locally recurrent metastatic melanoma". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 12 (1): 53–60. doi:10.2174/156802612798919187. PMID 22196271.
- "Definition of buthionine sulfoximine - National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary". 2011-02-02.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.