Butyl propionate
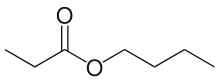
Butyl propionate is a butyl ester of propionic acid. This ester has the chemical formula CH3CH2COO(CH2)3CH3.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Butyl propionate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Butyl propanoate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.791 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UN number | 1914 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3CH2COO(CH2)3CH3 | |
| Molar mass | 130.187 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Pear drops, apple, strawberry, earthy, faintly sweet[1] |
| Density | 0.8754 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −89 °C (−128 °F; 184 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 146.8 °C (296.2 °F; 419.9 K)[1] |
| 1.5 mg/mL at 20 °C (poor)[1] | |
| Solubility | Miscible with alcohol, ether[1] |
| log P | 2.314[1] |
| Vapor pressure | 0.589 kPa 0.38 kPa at 20 °C[1] |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4014 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Very flammable |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H226 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P280, P303+P361+P353, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |
| Flash point | 90 °F (32 °C)[1] |
| 425 °C (797 °F)[1] | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Occurrence in nature
Butyl propionate is a plant metabolite, a human metabolite and an insect attractant. Butyl propionate is a natural ester found in Armenian apricot.[1]
Preparation
Butyl propionate is derived by esterification of propionic acid with butanol.[1]
- CH3CH2COOH + CH3(CH2)3OH ⇌ CH3CH2COO(CH2)3CH3 + H2O
Properties
Butyl propionate is a colorless liquid with a pear drops-like or apple-like odor. The liquid is less dense than water. Its vapor is 4.5 times denser than the air at the mean ocean level.[1]
Uses
Butyl propionate is used to make fragrances, perfumes and as a flavoring. It is also used in paints and primers for auto body or engine, appliance coatings (paints designed specifically for painting household items and vehicles like microwave ovens, refrigerators and automobiles), enamels, lacquers, and printing inks, as a solvent for adhesives and nitrocellulose, and in polymerization reactions for acrylic resins.[1]
Hazards and toxicity
Butyl propionate may irritate skin and eyes. Exposure to its vapor may cause eye and respiratory system irritation. Upon ingestion, causes abdominal pain and nausea. This chemical is very flammable. It may ignite even at ambient temperatures. Above 32 °C (90 °F), explosive mixtures with air may be formed. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a violent reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite this chemical and the reaction products. Upon catching a fire, irritating, toxic and suffocating gases may be produced, such as carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.[1]