Computer-aided technologies
Computer-aided technologies (CAx)[1] is the use of computer technology to aid in the design, analysis, and manufacture of products.
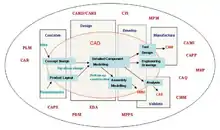
Illustration of the interaction of the various computer-aided technologies.
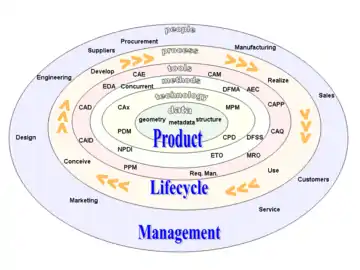
CAx tools in the context of product lifecycle management
Advanced CAx tools merge many different aspects of product lifecycle management (PLM), including design, finite element analysis (FEA), manufacturing, production planning, product
- Computer-aided design (CAD)
- Computer-aided architectural design (CAAD)
- Computer-aided engineering (CAE)
- Computer-aided fixture design (CAFD)
- Computer-aided innovation (CAI)
- Computer-aided industrial design (CAID)
- Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM)
- Computer-aided process planning (CAPP)
- Computer-aided requirements capture (CAR)
- Computer-aided rule definition (CARD)
- Computer-aided rule execution (CARE)
- Computer-aided software engineering (CASE)
- Computer-aided automation (CAA)
- Computer-assisted surgery (CAS)
- Computer-aided surgical simulation (CASS)
- Computational fluid dynamics (CFD)
- Component information system (CIS)
- Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM)
- Computer Numerical Controlled (CNC)
- Electronic design automation (EDA)
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
- Finite element analysis (FEA)
- Knowledge-based engineering (KBE)
- Knowledge Lifecylcle Management (KLM)
- Manufacturing process management (MPM)
- Manufacturing process planning (MPP)
- Material requirements planning (MRP)
- Manufacturing resource planning (MRP II)
- Product data management (PDM)
- Product lifecycle management (PLM)
- Virtual prototyping
See also
References
- Werner Dankwort, C.; Weidlich, Roland; Guenther, Birgit; Blaurock, Joerg E. (2004). "Engineers' CAx education—it's not only CAD". Computer-Aided Design. 36 (14): 1439–1450. doi:10.1016/j.cad.2004.02.011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.