Cytidine diphosphate glucose
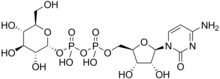
Cytidine diphosphate glucose, often abbreviated CDP-glucose, is a nucleotide-linked sugar consisting of cytidine diphosphate and glucose.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cytidine 5′-(α-D-glucopyranosyl trihydrogen diphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-Amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl} O3-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl] dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Other names
CDP-glucose | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H25N3O16P2 | |
| Molar mass | 565.318 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Biosynthesis
CDP-glucose is produced from CTP and glucose-1-phosphate by the enzyme glucose-1-phosphate cytidylyltransferase.
References
- Samuel G, Reeves P (2003). "Biosynthesis of O-antigens: genes and pathways involved in nucleotide sugar precursor synthesis and O-antigen assembly". Carbohydr. Res. 338 (23): 2503–19. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2003.07.009. PMID 14670712.
- Xue M. He and Hung-wen Liu (2002). "Formation of unusual sugars: Mechanistic studies and biosynthetic applications". Annu Rev Biochem. 71: 701–754. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135339. PMID 12045109.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.