Carboxylesterase 2
Carboxylesterase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CES2 gene.[5][6][7] It is a member of the alpha/beta fold hydrolase family.[8]
| CES2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CES2, CE-2, CES2A1, PCE-2, iCE, Carboxylesterase 2, CES-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605278 MGI: 3648740 HomoloGene: 128645 GeneCards: CES2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Carboxylesterase 2 is a member of a large multigene family. The enzymes encoded by these genes are responsible for the hydrolysis of ester- and amide-bond-containing drugs such as cocaine and heroin. They also hydrolyze long-chain fatty acid esters and thioesters. The specific function of this enzyme has not yet been determined; however, it is speculated that carboxylesterases may play a role in lipid metabolism and/or the blood–brain barrier system. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene.[7]
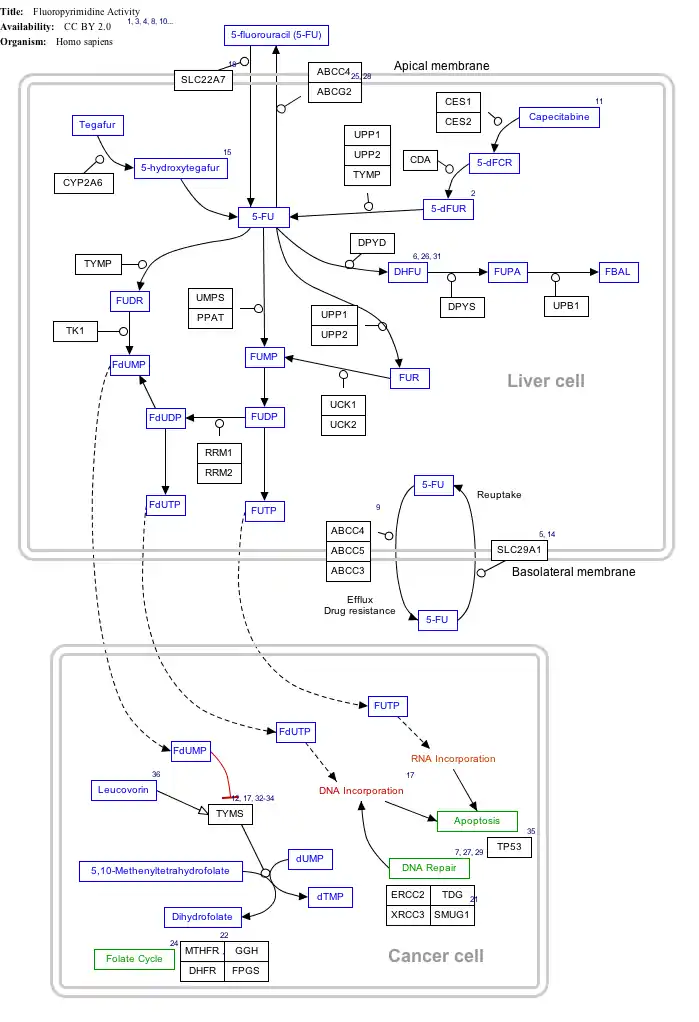
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.[§ 1]
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "FluoropyrimidineActivity_WP1601".
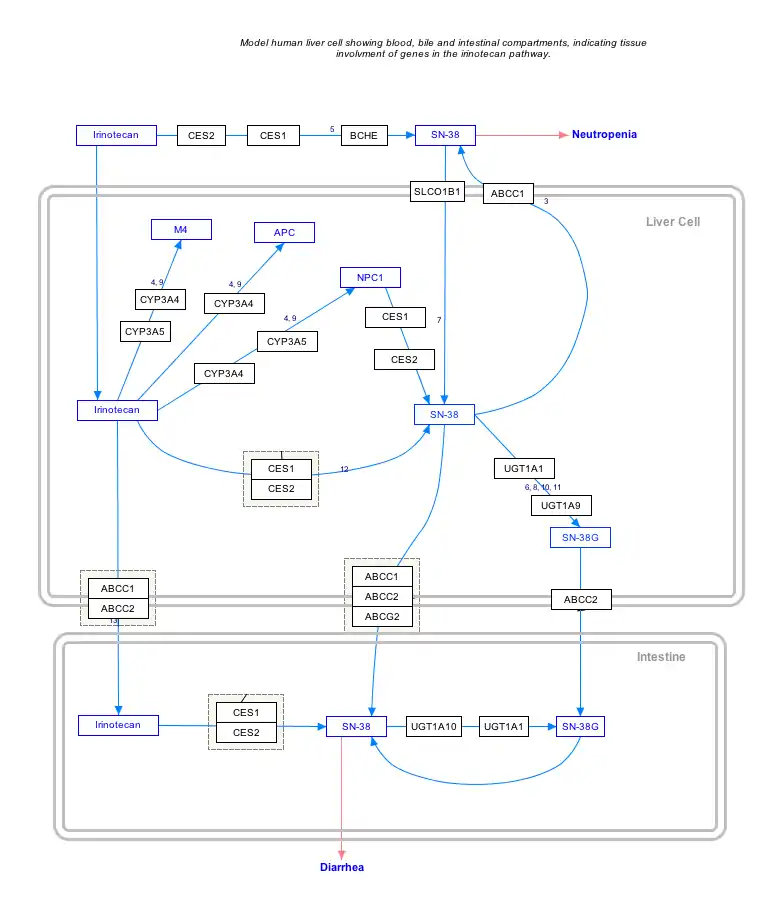
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "IrinotecanPathway_WP229".
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000172831 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000091813 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Pindel EV, Kedishvili NY, Abraham TL, Brzezinski MR, Zhang J, Dean RA, Bosron WF (June 1997). "Purification and cloning of a broad substrate specificity human liver carboxylesterase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of cocaine and heroin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (23): 14769–14775. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.23.14769. PMID 9169443.
- Schwer H, Langmann T, Daig R, Becker A, Aslanidis C, Schmitz G (April 1997). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel putative carboxylesterase, present in human intestine and liver". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 233 (1): 117–120. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6413. PMID 9144407.
- "Entrez Gene: CES2 carboxylesterase 2 (intestine, liver)".
- Imai T (June 2006). "Human carboxylesterase isozymes: catalytic properties and rational drug design". Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 21 (3): 173–185. doi:10.2133/dmpk.21.173. PMID 16858120.
Further reading
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–174. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–156. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Yan B, Matoney L, Yang D (September 1999). "Human carboxylesterases in term placentae: enzymatic characterization, molecular cloning and evidence for the existence of multiple forms". Placenta. 20 (7): 599–607. doi:10.1053/plac.1999.0407. PMID 10452915.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (November 2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Research. 10 (11): 1788–1795. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, et al. (March 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Research. 11 (3): 422–435. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Chagnon P, Michaud J, Mitchell G, Mercier J, Marion JF, Drouin E, et al. (December 2002). "A missense mutation (R565W) in cirhin (FLJ14728) in North American Indian childhood cirrhosis". American Journal of Human Genetics. 71 (6): 1443–1449. doi:10.1086/344580. PMC 378590. PMID 12417987.
- Saito S, Iida A, Sekine A, Kawauchi S, Higuchi S, Ogawa C, Nakamura Y (2003). "Catalog of 680 variations among eight cytochrome p450 ( CYP) genes, nine esterase genes, and two other genes in the Japanese population". Journal of Human Genetics. 48 (5): 249–270. doi:10.1007/s10038-003-0021-7. PMID 12721789.
- Wu MH, Chen P, Remo BF, Cook EH, Das S, Dolan ME (July 2003). "Characterization of multiple promoters in the human carboxylesterase 2 gene". Pharmacogenetics. 13 (7): 425–435. doi:10.1097/00008571-200307000-00008. PMID 12835618.
- Marsh S, Xiao M, Yu J, Ahluwalia R, Minton M, Freimuth RR, et al. (October 2004). "Pharmacogenomic assessment of carboxylesterases 1 and 2". Genomics. 84 (4): 661–668. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2004.07.008. PMID 15475243.
- Wu MH, Chen P, Wu X, Liu W, Strom S, Das S, et al. (September 2004). "Determination and analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotype structure of the human carboxylesterase 2 gene". Pharmacogenetics. 14 (9): 595–605. doi:10.1097/00008571-200409000-00004. PMID 15475733.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, Wellenreuther R, Schleeger S, Mehrle A, et al. (October 2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Research. 14 (10B): 2136–2144. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Charasson V, Bellott R, Meynard D, Longy M, Gorry P, Robert J (December 2004). "Pharmacogenetics of human carboxylesterase 2, an enzyme involved in the activation of irinotecan into SN-38". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 76 (6): 528–535. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2004.08.007. PMID 15592324. S2CID 23999721.
- Kim SR, Nakamura T, Saito Y, Sai K, Nakajima T, Saito H, et al. (2005). "Twelve novel single nucleotide polymorphisms in the CES2 gene encoding human carboxylesterase 2 (hCE-2)". Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 18 (5): 327–332. doi:10.2133/dmpk.18.327. PMID 15618752.
- Fox CA, Sapinoso LM, Zhang H, Zhang W, McLeod HL, Petroni GR, et al. (April 2005). "Altered expression of TFF-1 and CES-2 in Barrett's Esophagus and associated adenocarcinomas". Neoplasia. 7 (4): 407–416. doi:10.1593/neo.04715. PMC 1501154. PMID 15967118.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, Ota T, Nishikawa T, Yamashita R, et al. (January 2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Research. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Wang D, Zou L, Jin Q, Hou J, Ge G, Yang L (September 2018). "Human carboxylesterases: a comprehensive review". Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 8 (5): 699–712. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2018.05.005. PMC 6146386. PMID 30245959.
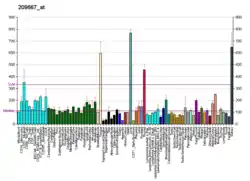
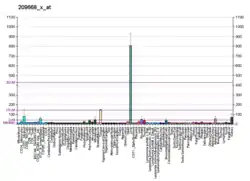
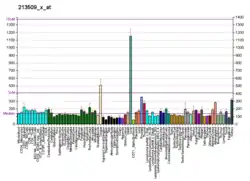
- "Tissue expression of CES2 - Summary - The Human Protein Atlas". www.proteinatlas.org. Retrieved 2022-09-30.