CHES (buffer)
CHES (N-cyclohexyl-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) is a buffering agent. CHES buffers have a useful range of pH 8.6–10.[1]
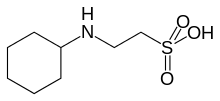 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Cyclohexylamino)ethane-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
N-Cyclohexyl-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid; N-Cyclohexyltaurine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.832 |
| MeSH | 2-(N-cyclohexylamino)ethanesulfonic+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H17NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 207.29 g·mol−1 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It typically appears as a white crystalline powder.
Effect of impurities
Commercial prep of CHES (and other sulfonylethyl buffers like MES, BES, and PIPES) can contain a contaminant oligo(vinylsulfonic acid) (OVS), which is a polyanionic mimic of RNA, and can be a potent (pM) inhibitor of RNA binding proteins and enzymes.[2]
References
- "Good's buffers (biological buffers)" (PDF).
- Smith, Bryan D.; Soellner, Matthew B.; Raines, Ronald T. (2003). "Potent Inhibition of Ribonuclease A by Oligo(vinylsulfonic Acid)". Journal of Biological Chemistry. Elsevier BV. 278 (23): 20934–20938. doi:10.1074/jbc.m301852200. ISSN 0021-9258.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.