C band (infrared)
In infrared optical communications, C-band (C for "conventional") refers to the wavelength range 1530–1565 nm, which corresponds to the amplification range of erbium doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs).[1] The C-band is located around the absorption minimum in optical fiber, where the loss reaches values as good as 0.2 dB/km, as well as an atmospheric transmission window (see figures). The C-band is located between the short wavelengths (S) band (1460–1530 nm) and the long wavelengths (L) band (1565–1625 nm). It includes the 50 GHz-spaced DWDM ITU channels 16 (1564.68 nm, 191.6 THz) to 59 (1530.33 nm, 195.9 THz).
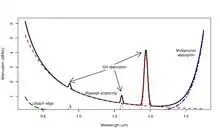
Absorption in fiber in the range 900–1700 nm with a minimum at the C-band
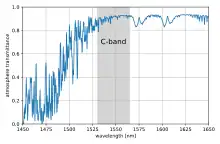
Transmittance of the atmosphere around the C-band
References
- Optical Fiber Communications article in rp-photonics' Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology (accessed Nov. 11 2010)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.