Cacodyl oxide
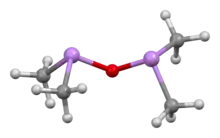
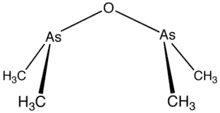
Cacodyl oxide is a chemical compound of the formula [(CH3)2As]2O. This organoarsenic compound is primarily of historical significance since it is sometimes considered to be the first organometallic compound synthesized in relatively pure form.[1][2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dimethylarsinous anhydride | |
| Other names
TL-297 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H12As2O | |
| Molar mass | 255.98 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
"Cadet's fuming liquid", which is composed of cacodyl and cacodyl oxide, was originally synthesized by heating potassium acetate with arsenic trioxide. It has a disagreeable odor and is toxic.
The molecular structure of [Ph2As]2O (Ph = phenyl), the tetraphenyl analogue of cacodyl oxide, has been established by X-ray crystallography.[3]
See also
References
- Elschenbroich, C. (2006). Organometallics. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 9783527293902.
- Seyferth, D. (2001). "Cadet's Fuming Arsenical Liquid and the Cacodyl Compounds of Bunsen". Organometallics. 20 (8): 1488–1498. doi:10.1021/om0101947.
- Doerrer, Linda H.; Green, Jennifer C.; Green, Malcolm L. H.; Haiduc, Ionel; Jardine, Christian N.; Pascu, Sofia I.; Silaghi-Dumitrescu, Luminita; Watkin, David J. (2000). "Group 6 transition metal carbonyl complexes with chalcogen-bridged diarsenic(III) ligands". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (19): 3347–3355. doi:10.1039/b005269h.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.