Mother lode
Mother lode is a principal vein or zone of gold or silver ore. The term is also used colloquially to refer to the real or imaginary origin of something valuable or in great abundance.
Term
The term probably came from a literal translation of the Spanish veta madre, a term common in old Mexican mining. Veta madre, for instance, is the name given to an 11-kilometre-long (6.8 mi) silver vein discovered in 1548 in Guanajuato, New Spain (modern-day Mexico).[1]
California Mother Lode
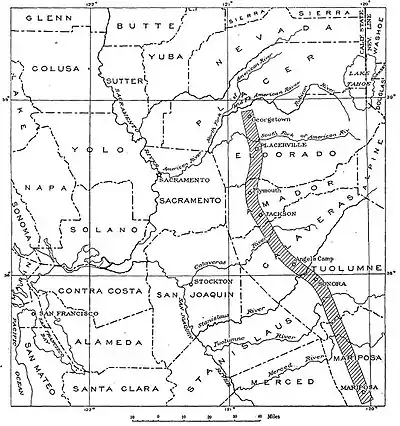
In the United States, Mother Lode is most famously the name given to a long alignment of hard-rock gold deposits stretching northwest-southeast in the Sierra Nevada of California,[2] bounded on the east by the Melones Fault Zone.[3] It was discovered in the early 1850s, during the California gold rush. The California Mother Lode is a zone from 1.5 to 6 kilometres (0.93 to 3.73 mi) wide and 190 kilometres (120 mi) long, between Georgetown on the north and Mormon Bar on the south.
The Mother Lode coincides with the suture line of a terrane, the Smartville Block.[4] The zone contains hundreds of mines and prospects, including some of the best-known historic mines of the gold-rush era. Individual gold deposits within the Mother Lode are gold-bearing quartz veins up to 15 metres (49 ft) thick and a few thousand feet long. The California Mother Lode was one of the most productive gold-producing districts in the United States. Now it is known as a destination for tourism and for its vineyards.[5]
As with most gold rushes, the California gold rush started with the discovery of placer gold in sands and gravels of streambeds, where the gold had eroded from hard-rock vein deposits. Placer miners followed the gold-bearing sands upstream to discover the source in the bedrock. This source was the "mother" of the gold in the river and so was dubbed the "mother lode".
References
- Alan M. Bateman (1942) Economic Mineral Deposits. New York: Wiley, p.465-466.
- Knopf, Adolph (1929). "The Mother Lode System of California, USGS Professional Paper 157". USGS. doi:10.3133/pp157. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - "Ophir District". USGS. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- McPhee, John (2010). Assembling California. Farrar, Straus and Giroux. p. 58. ISBN 9780374706029.
- A.H. Koschman and M.H. Bergendahl (1968) Principal Gold-Producing Districts of the United States. US Geological Survey, Professional Paper 610, p.55

