Canolol
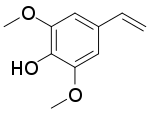
Canolol is a phenolic compound found in crude canola oil.[1][2] It is produced by decarboxylation of sinapic acid during canola seed roasting.[3][4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Ethenyl-2,6-dimethoxyphenol | |
| Other names
2,6-Dimethoxy-4-vinylphenol 4-Vinyl-2,6-dimethoxyphenol 4-Vinylsyringol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12O3 | |
| Molar mass | 180.203 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Canolol: A Promising Chemical Agent against Oxidative Stress. Annia Galano, Misaela Francisco-Márquez and Juan R. Alvarez-Idaboy, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2011, 115 (26), pages 8590–8596, doi:10.1021/jp2022105
- 4-Vinyl-2,6-dimethoxyphenol (canolol) suppresses oxidative stress and gastric carcinogenesis in Helicobacter pylori-infected carcinogen-treated Mongolian gerbils. Cao X, Tsukamoto T, Seki T, Tanaka H, Morimura S, Cao L, Mizoshita T, Ban H, Toyoda T, Maeda H and Tatematsu M, Int J Cancer., 1 Apr 2008, 122(7), pages 1445-1454, PMID 18059022
- Antioxidant canolol production from a renewable feedstock via an engineered decarboxylase. Krista L. Morley, Stephan Grosse, Hannes Leischa and Peter C. K. Lau, Green Chem., 2013,n15, pages 3312-3317, doi:10.1039/C3GC40748A
- Isolation and Identification of a Potent Radical Scavenger (Canolol) from Roasted High Erucic Mustard Seed Oil from Nepal and Its Formation during Roasting. Kshitij Shrestha, Christian V Stevens, Bruno De Meulenaer, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2012, 60 (30), pp 7506–7512, doi:10.1021/jf301738y
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.