Carol of the Bells
"Carol of the Bells" is a popular Christmas carol which is based on the Ukrainian song called "Shchedryk" (Ukrainian: Щедрик). The "Carol of the Bells" uses the original melody from "Shchedryk," written by the Ukrainian composer Mykola Leontovych in 1914.[1]
| "Carol of the Bells" | |
|---|---|
| Christmas carol by Mykola Leontovych | |
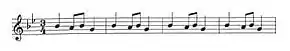 The four-note motif (shown four times) | |
| Text | by Peter J. Wilhousky |
| Based on | "Shchedryk" |
| Composed | 1919 |
| ⓘ | |
Ukrainian "Shchedryk" was adapted as an English Christmas carol, "Carol of the Bells", by Peter J. Wilhousky of NBC Radio, following a performance of the original song by the Ukrainian National Chorus at Carnegie Hall on October 5, 1922. Peter J. Wilhousky, American composer, music educator, and choral conductor of Ukrainian descent, wrote the lyrics in English.
The Ukrainian music is in the public domain; Wilhousky's lyrics, however, are under copyright owned by Carl Fischer Music.
The music is based on a four-note ostinato and is in 3
4 time signature, with the B-flat bell pealing in 6
8 time. The carol is metrically bistable, and a listener can focus on either measure or switch between them. It has been adapted for many genres, including: classical, metal, jazz, country music, rock, trap, and pop. The piece also features in films, television shows, and parodies.
Background
Origins

The conductor of the Ukrainian Republic Capella, Oleksander Koshyts (also spelled Alexander Koshetz) commissioned Leontovych to create the song based on traditional Ukrainian folk chants, and the resulting new work for choir, "Shchedryk", was based on four notes Leontovych found in an anthology.[2]
The original folk story related in the song was associated with the coming New Year, which, in pre-Christian Ukraine, was celebrated with the coming of spring in April. The original Ukrainian title translates to "the generous one"[3] or is perhaps derived from the Ukrainian word for bountiful (shchedryj),[2] and tells a tale of a swallow flying into a household to proclaim the bountiful year that the family will have.[4]
With the introduction of Christianity to Ukraine and the adoption of the Julian calendar, the celebration of the New Year was moved from April to January, and the holiday with which the chant was originally associated became Malanka (Ukrainian: Щедрий вечір, Shchedry vechir), the eve of the Julian New Year (the night of January 13–14 in the Gregorian calendar). The songs sung for this celebration are known as Shchedrivky.
The song was first performed by students at Kyiv University in December 1916, but the song lost popularity in Ukraine shortly after the Soviet Union took hold.[4] It was introduced to Western audiences by the Ukrainian National Chorus during its 1919 concert tour of Europe and America, where it premiered in the United States on October 5, 1922,[5] to a sold-out audience at Carnegie Hall.[2] The original work was intended to be sung a cappella by mixed four-voice choir.[4]
Two other settings of the composition were also created by Leontovych: One for women's choir (unaccompanied) and another for children's choir with piano accompaniment. These are rarely performed or recorded.
English lyric versions
Wilhousky rearranged the melody for orchestra with new lyrics for NBC radio network's symphony orchestra, centered around the theme of bells because the melody reminded him of hand bells,[4] which begins "Hark! How the bells".[6] It was first aired during the Great Depression,[4] and Wilhousky copyrighted the new lyrics in 1936 and also published the song, despite the song having been published almost two decades earlier in the Ukrainian National Republic.[2] Its initial popularity stemmed largely from Wilhousky's ability to reach a wide audience as his role as arranger for the NBC Symphony Orchestra. It is now strongly associated with Christmas because of its new lyrics, which reference bells, caroling, and the line "merry, merry, merry, merry Christmas".[2]
"Ring, Christmas Bells", an English-language variant featuring nativity-based lyrics, was written by Minna Louise Hohman in 1947.[7] Two other versions exist by anonymous writers: one from 1957 titled "Come Dance and Sing" and one from 1972 that begins "Hark to the bells".[6]
American recordings by various artists began to surface on the radio in the 1940s.[2] The song gained further popularity when an instrumental was featured in television advertisements for Andre champagne in the 1970s. "Carol of the Bells" has been recorded into over 150 versions and re-arrangements for varying vocal and instrumental compositions.[8]
Notable recordings
- 1962: The Ray Conniff album We Wish You a Merry Christmas included the "Ring Christmas Bells" version by Minna Louise Hohman.[9][10][11]
- 1988: Mannheim Steamroller recorded a prog-rock version on their second Christmas studio album A Fresh Aire Christmas, which has sold over 6 million copies in the U.S., making it one of the best-selling Christmas albums of all time.[12]
- 1990: Wynton Marsalis recorded a syncopated version on the album Crescent City Christmas Card with the role of the bells carried by brass.[13]
- 1990: Composer John Williams conducted a version for the Home Alone: Original Motion Picture Soundtrack. Williams' "Carol of the Bells" charted at number 86 on Billboard's Greatest of All Time Holiday 100 chart, which measured chart data 1958–2016.[14]
- 1993: David Foster wrote a rendition for his album The Christmas Album. On Billboard's Greatest of All Time Holiday 100 chart, which measured chart data 1958–2016, Foster's take on "Carol of the Bells" charted at number 77.[15]
- 1995: Savatage recorded "Christmas Eve/Sarajevo 12/24", an instrumental, heavy-metal medley of "God Rest Ye Merry, Gentlemen" and "Carol of the Bells". The song became the No. 1 requested song on the influential New York station WPLJ, which led to the band gaining label support to form Trans-Siberian Orchestra and create a new album based on the song.[16]
- 2005: Nox Arcana performed this song on their album Winter's Knight that reached No. 8 on the Billboard Charts the following year.[17]
- 2007: The Bird and the Bee released this song on a non-album single.[18]
- 2011: The Piano Guys published a cello arrangement of the song on YouTube, and it has garnered over 30 million views. A mashup arrangement of the song with "God Rest Ye Merry Gentlemen" was featured on their Christmas album A Family Christmas, which charted at No. 20 of US Billboard 200.[19]
- 2012: Metal band August Burns Red's "breakdown-infused" version of the song was used in a Christmas-themed promotional ad for Frank Miller's film The Spirit, although the song did not appear in the film.[20]
- 2012: Pentatonix covered the song on their album PTXmas, one of the highest selling Christmas albums of 2013.[21]
- 2013: Marillion released an extended version for charity.[22]
- 2013: Christopher Drake used the song as the Joker's main theme in Arkham Origins
- 2017: Lindsey Stirling released her version on her holiday album Warmer in the Winter.[23]
- 2017: Lena Meyer-Landrut released her version on the official album to the television show Sing meinen Song – Das Weihnachtskonzert, Vol. 4.[24]
- 2021: Mantikor released a German metal & rock version on the official Rookies & Friends, Vol. 3 XMAS Edition Compilation.[25]
In popular culture
- The song appears in the 1990 film Home Alone as arranged by John Williams.[26] In 2018, this version charted at No. 20 on the Swedish Heatseeker chart.[27]
- The Muppets' 2009 parody of the song climaxes with a large bell (set up by Animal) falling on the increasingly frenetic Beaker,[28] which quickly became a viral video that Christmas season.[29]
Charts
Pentatonix version
| Chart (2013–2014) | Peak position |
|---|---|
| US Holiday 100 (Billboard)[30] | 66 |
Mantikor version
| Chart (2021) | Peak position |
|---|---|
| DE Deutsche Compilationcharts[31] | 3 |
See also
References
- Korchova, Olena (December 17, 2012). "Carol of the Bells: Back to the Origins". The Ukrainian Week. Archived from the original on October 28, 2018.
- Peresunko, T. (2019). "100 years of Ukraine's cultural diplomacy: European mission of Ukrainian Republican Chapel (1919-1921)". Kyiv-Mohyla Humanity Journal. 5: 69–89. doi:10.18523/kmhj189010.2019-6.69-89. S2CID 214231721.
- Cited by
- Collins, Andrew (2010). "Carol of the Bells". Stories Behind the Greatest Hits of Christmas. Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan. p. 39. ISBN 9780310327950.
- Peterson, Lottie (December 20, 2015). "The creation of carols: A look at the history behind 7 beloved holiday songs". The Deseret News. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- "Carol of the Bells performance history". carnegiehall.org. New York, NY: Carnegie Hall. Retrieved November 15, 2022.
- Crump, William D. (2013). "Carol of the Bells" in The Christmas Encyclopedia. 3rd Edition. McFarland & Company, Inc. Publishers: Jefferson, NC. p. 62. ISBN 9780786468270.
- Nobbman, Dale V. (2000). Christmas Music Companion Fact Book: The Chronological History of Our Most Well-Known Traditional Christmas Hymns, Carols, Songs And the Writers & Composers Who Created Them. Centerstream Publishing: Anaheim Hills, CA. p. 91. ISBN 1574240676.
- Wytwycky, Wasyl (updated 2010). "Leontovych, Mykola". Internet Encyclopedia of Ukraine. Retrieved December 23, 2015.
- Bratcher, Melissa (December 9, 2016). "Music Review: Ray Conniff And The Ray Conniff Singers, The Complete Columbia Christmas Recordings". popshifter. Retrieved December 14, 2017.
- "Ring Christmas Bells Chords and Lyrics – Ray Conniff". topchristianlyrics.com. November 18, 2009. Retrieved December 14, 2017.
- "The Carol of the Bells: A personal meaning and reflection for this Christmas Season". December 23, 2008. Retrieved December 14, 2017.
- "RIAA Searchable Database". Recording Industry Association of America. Archived from the original on April 16, 2013. Retrieved December 24, 2015.
- Thompson, Matt (December 17, 2015). "The Ironic Intensity of 'Carol of the Bells'". The Atlantic. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- "Greatest of All Time Holiday 100 Songs". Billboard. November 18, 2021. Retrieved November 24, 2022.
- "Greatest of All Time Holiday 100 Songs". Billboard. November 18, 2021. Retrieved November 24, 2022.
- Journal, Neil Shah | Photography by Ryan Henriksen for The Wall Street (December 3, 2015). "How the Trans-Siberian Orchestra Became a Holiday Hit Machine". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- "Billboard Music Charts". Billboard. Retrieved January 27, 2007.
- "The Bird And The Bee – Carol Of The Bells". discogs. Retrieved December 1, 2017.
- ThePianoGuys (December 19, 2011), Carol of the Bells (for 12 cellos) - The Piano Guys, archived from the original on December 12, 2021, retrieved October 30, 2017
- "August Burns Red's JB Brubaker On Being A Part Of 'The Spirit' Of Christmas". MTV. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- Legg, Carlyn. "Music for the holiday season". The East Carolinian. Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- Savić, Nikola (December 15, 2013). "Marillion Release 'The Carol Of The Bells' Christmas Single". Prog Sphere. Retrieved December 16, 2015.
- "ALBUM REVIEW: Lindsey Stirling - 'Warmer In The Winter'". CelebMix. October 19, 2017. Retrieved October 23, 2017.
- "laut.de-Kritik "Im Kopf rieselt leise der Schnee."". Laut.de. November 28, 2017. Retrieved December 1, 2017.
- Scherer, Nicole (November 16, 2021). "Rookies&Friends Sampler – Vol. 3 XMAS Edition". Vollgas Richtung Rock (in German). Retrieved November 30, 2022.
- Paget, Antonia (December 20, 2015). "Have-a-go singers who formed a Christmas choir to perform concert in Walton". Liverpool Echo. Retrieved December 23, 2015.
- "Veckolista Heatseeker, vecka 52, 2018" (in Swedish). Sverigetopplistan. Retrieved April 24, 2021.
- Lascala, Marisa (July 4, 2014). "The Muppets' Fourth of July Performance Will Be Incredible Because Of Course It Will". Bustle. Retrieved December 23, 2015.
- Macleod, Duncan (December 26, 2009). "The Muppets sing Carol of the Bells". Inspiration Room. Retrieved December 23, 2015.
- "Pentatonix Chart History (Holiday 100)". Billboard. Retrieved August 5, 2021.
- Official German Copilation Charts (December 3, 2021). "Chart Position #3, Week December 3, 2021 - December 9, 2021 ". Offizielle Deutsche Charts. Retrieved December 04, 2021.