Castle of Ayora
The Castle of Ayora is located at an elevation of 552 (1,811 ft) metres above mean sea level (mamsl),[1] in the centre of Ayora, a Valencian town. Built probably in the mid 13th century, after the Reconquista, on an ancient Arabian building. The architectural ensemble was composed of the four-storey residence-palace, two fortified towns, and one large keep, as well as other rooms for the soldiers and serfdom, aljibes (European Middle Ages castle cisterns that collected the rain water to provide drinking water to the castles) and gardens. This was surrounded by around 0.62 miles (1,000 m) of defensive walls and defensive towers.
The castle was reduced to ruins by the troops of Philip V of Spain, in the War of the Spanish Succession, but its profile and its vast size are still noticeable. The keep, of square plan, the Puerta Falsa (Fake Door), commissioned by the Marchioness of Cenete in the 16th century on which it was her coat of arms, as well as paintings, defensive walls, buckets, moats, and cisterns, stand out in the remains of the castle.[2]
Since 2006, it is a Bien de Interés Cultural (property of cultural interest) with reference RI-51-0010507.[3]

History
It is of Muslim origin and was rebuilt in its entirety in the 13th century after the Valle de Cofrentes was regained by the Aragonese troops[4] between 1239 and 1243. With the signing of the Treaty of Almizra in 1244 between the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon, the Castilians take over Ayora. Ayora is in hands of the Aragonese again, as a war reparation, by the Treaty of Campillo signed in 1281 between Alfonso X the Wise of Castile and Peter III the Great of Aragon.
Ayora was part of The Kingdom of Valencia once again by decision of James II the Just, the king of Aragon, by means of the Treaty of Elche in 1305.
The first reference of the castle comes precisely from the Muslim geographer Muhammad al-Idrisi who mentioned it in passing in the 12th century.
With the decree of expulsion of the Moriscos in 1609, the valley was practically depopulated, after they had rebelled against the royal power.
During the 14th century and 15th century, Ayora was a place of feudal manor, it was property of the admiral of Aragon Bernardo de Sarriá. In 1492 it was bought by Don Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar y Mendoza (son of Cardinal Mendoza), first Marquis of Cenete, who died in 1523. His daughter Mencía de Mendoza, Marchioness of Cenete, (Jadraque, 1508 - Valencia, 1554) inherited the manor, but when she died without descendants it passed into the hands of her sister María, who was married Diego Hurtado de Mendoza, Duke of the Infantado, being united to its dominions until 1837, when the feudal regimes were abolished.
During the 16th century and 17th century, the castle underwent important alterations in order to refurbish it as a palace, including the construction of the so-called Puerta Falsa, commissioned by Lady Mencía de Mendoza.
The castle is practically in ruins since in 1707 the troops of Philip V of Spain, under the command of the Count of Pinto, took by assault, looting and burning the town and the castle, and people left the castle. In 1797 the botanist Antonio Jose Cavanillles gave a description of it and presented it as a ruined and destroyed place (observations collected by the geographer and botanist Cavanilles in his work "Observaciones...del Reino de Valencia"). In 1812 the French occupied the valley and finished with the remains of the castle that were left.
The town of Ayora, located at the foot of the castle, was in turn walled, having three doors or accesses: the Portal of the Virgen de Gracia, the Portal of Santa Lucia, and the Portal of Palaz or San Nicolás.
Architecture
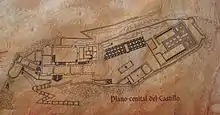
Built on a lengthened floor plan, it is adapted to the land on which it is raised. Just in the middle of the castle and being dominant over the landscape, a four-sided tower[1] is erected. Made using masonry and ashlar construction procedures, there are still remainders of rammed earth from some prior Muslim structures.
It has two strongholds. The bigger one known as Plaza de Armas with geometrically designed pebble pavement and the smaller one, located in the south, considered to be the patio of the previous fortress/palace of the Marchioness of Cenete.
The castle was surrounded by 6-metre-high and 900-metre-long[1] ramparts. Among the ruins, remains from several four-cornered towers and from a semicircular one may be found. Moreover, there are rests of antique rooms.[3]
The castle had two entrances. The Northern one was accessible by crossing the well-known Barrio Alto (The High Suburb). The Southern one by the well-known Puerta Falsa (16th Century) which straightaway gave way to the palace.
Despite its current difficult access, it used to be the main entry to the castle. It is known as Puerta Falsa, due to the fact that at the present time it does not play that role, since a quarry was placed before it.
The door had a semicircular arch and it was built with reddish limestone ashlars. The door is framed by an asymmetrical stone coving in the shape of the architectonic adornment called alfiz, above which was supposedly the coat of arms of the owners of the castle. Nowadays, its location is unknown.
The coat of arms was likely to be of the Marquisate of Cenete. On the right side of the door there are remains of what presumably was a baseboard ornamenting the wall and simulating a column built in the wall with a capital at the top and a column base. Above the door there are two corbels that held a machicolation, currently missing, which protected the entry from attacks.
References
- Castillos, torres y fortalezas de la Comunidad Valenciana. Prensa Valenciana. 1995. p. 679.
- "Castillo de Ayora. Palacio - Fortaleza del Duque del Infantado". ayora.es.
- "Secció 1a. Béns d'interés cultural - Generalitat Valenciana". www.ceice.gva.es.
- Trobes de mossèn Jaume Febrer, 17th century manuscript