Cefonicid
Cefonicide (or cefonicid) is a cephalosporin antibiotic.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H18N6O8S3 |
| Molar mass | 542.56 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
It has a density of 1.92g/cm3.
Synthesis
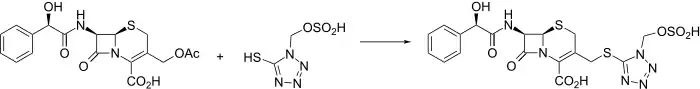
Injectable semi-synthetic cephalosporin antibiotic related to cefamandole, q.v.
Cefonicid is synthesized conveniently by nucleophilic displacement of the 3-acetoxy moiety of 1 with the appropriately substituted tetrazole thiole 2. The mandelic acid amide C-7 side chain is reminiscent of cefamandole.
See also
References
- Saltiel E, Brogden RN (September 1986). "Cefonicid. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacological properties and therapeutic use". Drugs. 32 (3): 222–59. doi:10.2165/00003495-198632030-00002. PMID 3530703.
- DE 2611270, Berges, David Alan, "Cephalosporin-Derivate [Cephalosporin derivatives]", published 1976-09-30, assigned to SmithKline Corp.
- D. A. Berges, U.S. Patent 4,048,311 (1977 to Smith Kline).
- U.S. Patent 4,093,723, U.S. Patent 4,159,373 (1978, 1979 both to Smith Kline).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.