Château de Maulnes
The château de Maulnes, is a 16th-century, Renaissance-style château located in Cruzy-le-Châtel in the department of Yonne, France.
| Château de Maulnes | |
|---|---|
.JPG.webp) The pentagonal house (center) and semicircular commons (left) of the château as seen from the south-west (rear view) | |
| Nearest city | Auxerre |
| Coordinates | 47°53′25.47″N 4°12′53.05″E |
| Built | 14th century |
| Built for | Antoine de Crussol and Louise de Clermont |
| Original use | Château |
| Restored | ongoing since 2001 |
| Current use | Tourist attraction and historical research |
| Architectural style(s) | Renaissance |
| Owner | General Council of the Yonne (since 1997) |
| Designated | 1942 [1] |
 Location of Château de Maulnes in France | |
This château was built between 1566 and 1573 and has several unique design features. For example, it has a novel pentagonal-shaped house and is buttressed by five towers, and has a centrally located well surrounded by a spiral staircase.
During the 20th century, the château was in an advanced state of disrepair. In 1942, the château was classified as a historic monument and in 1997 it was purchased by the Conseil General of Yonne. It has since been the focus of historical and archaeological research and restoration. In 2005, the château was made open to the public.
History
The "motte of Maulnes"
The site on which the château stands is believed to have been occupied since the Neolithic era. The earliest reference to the area is found in a book written in the year 863 called "Molnitum".
A fortified structure, known as the "motte of Maulnes", was built in a clearing within the forest Maulnes, by the counts of Tonnerre in the 13th century. The time-frame has been confirmed by references made in historical writings as well as research using aerial photography. This structure is thought to have facilitated the counts in hunting activities, such as in the company of distinguished guests including the Duke of Burgundy Philip the Bold, who came to hunt in 1366 and 1374.
In 1411, a quarrel broke out between the Count of Tonnerre (Louis II of Chalon-Arlay) and the Duke of Burgundy (John the Fearless). As a consequence, the Burgundian troops invaded the county and destroyed this structure, as well as others.
The project


A century and a half later, after the death of her first husband, the countess of Tonnerre, Louise de Clermont, married Antoine de Crussol, Duke of Uzes, Both were influential and well known figures, close to the court of France as well as the Queen herself, Catherine de Medici.
In 1566, the couple decided to build a château in the forest Maulnes where the "motte of Maulnes" once stood. By this time, the sixty-two year old Louise had considerable exposure to and appreciation for architecture. For example, her brother, Antoine III of Clermont, entrusted the architect Sebastiano Serlio to building him a château in Ancy-le-Franc, near Maulnes, about 25 years earlier.
With the signing of the Edict of Amboise in 1563, France enjoyed a brief period of peace from internal religious wars, allowing for a large-scale project, such as building the Château de Maulnes, to come to fruition.
Antoine de Crussol, who became Duke of Uzes in May 1565, no longer had a residence worthy of his rank in the county. The château would stand as a symbol of his newly acquired power, if not by its size, then by its beauty and architectural originality.
The location of the château in the forest was likely chosen due to nearby hunting opportunities as well as the economic incentive for extracting timber from the vast forests of the region. At the time, the sale of firewood to Paris was the most important resource of the region.
The construction (1566 - 1573)
On May 7, 1566, Antoine de Crussol signed a notarized contract to hire a master mason and a master carpenter and provided them with detailed plans of the Château de Maulnes. While there is much speculation regarding the possible architect for the project, the designer is not known.
In February 1568, following a period of religious unrest, the Prince of Conde's army occupied the suburbs of Tonnerre and besieged the city, relenting with the payment of a ransom. In November, the Catholic troops seized Noyers (Yonne), and about a year later the army of Marshal de Cosse arrived and restored the peace in Tonnerre.

Despite these setbacks, progress on the construction continued. In September 1569, Louise de Clermont moved to Maulnes, and furnished the château. In January 1570, Antoine de Crussol joined her in the completed château. The second project, constructing the adjoining buildings, may have started in August 1570, after the departure of Crussol who joined the French court in later life.
In 1572, Antoine de Crussol was made peerage of France, for his Duchy of Uzes. During this time, tensions in the country were particularly high between Catholics and Protestants. On August 24, 1572, Anthoine's brother Galiot became one of the victims of the massacre of St. Bartholomew. From January to July 1573, Antoine de Crussol participated in the siege of La Rochelle (1572–73). He returned to Château de Maulnes exhausted and ill and died August 14, 1573.
The Clermont-Tonnerre period (1573 - 1697)
Once again a widow, Louise de Clermont spent her remaining years between Paris, Tonnerre, Ancy-le-Franc and Maulnes. After May 1575, she did not return to Maulnes and entrusted the building to two men. In 1576, the Château de Maulnes, was listed in a publication as one of the top 30 exceptional buildings in France.[2]
In the following years, Louise faced legal trials filed against her as well as the estates of her deceased husbands. At 92 years old, she died in May 1596 in the Hotel-Dieu de Tonnerre. Louise de Clermont died childless and with unresolved legal problems. In March 1606, her great-nephew and heir Charles-Henri de Clermont reached an agreement with the creditors. After a paying out a settlement, he became Count of Tonnerre, Cruzy and Maulnes. In 1610 Charles-Henri made enhancements to the ceiling in the great hall.
Charles-Henri also divided the regions of Maulnes and Cruzy, and made his youngest son marquess and his oldest son the count of Clermont and Tonnerre.
Despite these preparations for his sons, after his death in 1640, his eldest son François de Clermont claimed that some of the possessions of his brother Roger, to have always belonged to Tonnerre County. That same year, his representative took possession of the château de Maulnes. It is not known if it was inhabited by either brother, however an engraving of Israel Silvestre in 1650 suggests that it was in a state of neglect. With respect to the ownership of the château, in 1658 a judgment of parliament sided with the younger brother Roger, Marquess of Cruzy.
A fortified structure, known as the "motte of Maulnes", was built in a clearing within the forest Maulnes, by the counts of Tonnerre in the 13th century. The time-frame has been confirmed by references made in historical writings as well as research using aerial photography. This structure is thought to have facilitated the counts in hunting activities, such as in the company of distinguished guests including the Duke of Burgundy Philip the Bold, who came to hunt in 1366 and 1374.
Between 1650 and 1670, In 1647 Roger returned from the armies of Flanders and between 1650 and 1670 he made modifications and repairs to château de Maulnes.
The Louvois period (1697 - 1844)

Between 1683 and 1685, François-Michel le Tellier, Marquis de Louvois bought Tonnerre county from François-Joseph Clermont, the grandson of Francis and the grand-nephew of Roger. Louvois was well known for his role as the French Secretary of State for War.
Louvois died in 1691 and his widow, Anne de Souvré maintained possession of Tonnerre county. In June 1697, Anne bought Maulnes and Cruzy from Roger's son, who was experiencing financial difficulties, and thus taking possession of the château de Maulnes and reuniting Charles-Henri's divided estate.
Anne de Souvré drew a detailed map of the forest Maulnes and died in December 1715. The estate is settled six years later, and Maulnes was again abandoned.
In 1721, the eldest son of Louvois, Michel-François Le Tellier marquis Courtanvaux, inherited Tonnerre County, but he died soon thereafter. His daughter, Anne-Louise de Noailles, received temporary guardianship until his two-year-old son, Francis Tellier Caesar Courtanvaux, became an adult.
In 1723, the royal council of finance authorized timber to float from Maulnes to Paris by the Armançon, Yonne and the Seine rivers. As a consequence, a small community of workers formed around the château. As an adult, Francis continued the timber operations. In 1775, the timber merchants near the château received permission from the Marquis to start a glassworks industry, which was more profitable than selling timber. This industry transformation significantly changed the landscape of Maulnes with the gradual clearing of the forest and the growth of the community.
In 1781, the Marquis died with no direct heir. His cousin Louis-Sophie Le Tellier Souvré, son of François-Louis Le Tellier, became Count of Tonnerre. He died in debt four years later and his widow Jeanne Marie Henriette Bombelles Victory supervised the estate on behalf of her two-year-old son. Both survived the French Revolution and the abolition of French feudalism and regained the property and she managed it until her death in 1822.
In 1806, a note drafted by the subprefect of Tonnerre described the processes and in the production of Maulnes glassware, specifically mentioning production of 300,000 bottles per year. This production could only occur 6 months out of the year due to timber limitations of the forest of Maulnes.
When he took over the management of glassware in 1819, Louis Le Tellier Souvré became a peer of France under the Restoration. In 1804, his son, Auguste Felicite Michel Le Tellier, married Athénaïs Grimaldi of Monaco, daughter of Joseph Grimaldi and niece of the Prince of Monaco Grimaldi Honoré IV.
In 1819, production doubled and the local glassware industry was employing a hundred workers, in addition to the loggers and valets.
In 1824 the Maulnes estate was rented to a master came glassmaker from Bayel, François Vallory. In 1834, the financially ruined Marquis de Louvois sold Maulnes, including the château, to the glassmaker. In 1844, François closed the estate, facing his own financial difficulties.
.JPG.webp)
Period of abandonment (1844 - 1997)
The château and the surrounding land was sold in 1851 to Gabriel Knight, a banker from Châtillon-sur-Seine, who abandoned the château. After his death in 1866, succession documents describe the buildings "in poor condition". In the 1880s, some repairs were undertaken. After the bankruptcy of Adrian Knight, the Maulnes estate is purchased by the Prunier family in 1898. It then passed into the hands of the industrialist Ferdinand Serres and his son, who own it from 1918 to 1960. It is believed these successive owners were more interested in the land and woods surrounding the château, since the château itself was not maintained and gradually falls into serious disrepair during this period..
On 11 July 1942, le château de Maulnes was classified by France's Service des Monuments Historiques, who unsuccessfully attempted repairs in 1943 and 1944. In 1960, the deed of sale indicates "a château and outbuildings, all in ruins". The château, without the land was purchased by the Friends of Maulnes Company and for the first time, a large backup funded plan was implemented. In 1964, a work permit was granted to repair the crumbling façades. Fundraising continued until 1969.
But the company suddenly ended the campaign and deterioration worsened with the storms in 1979 and 1981–1982. In 1985, a decree compelled the owner to perform the restoration work; they are led to office in 1987. Finally in 1997, the General Council of the Yonne acquired Maulnes after an expropriation procedure.

The period of rediscovery (1997 -)
In 1997 a scientific committee is set up to organize multidisciplinary research required to understand Maulnes. While historians studying the archives relating to the château and its sponsors, archaeologists of the Centre for Medieval Studies at Auxerre performed excavations and research, both in the château and its surroundings. For four years, the research focused on various themes such as the relationship between the château and the Maulnes forest and the hydrogeological study of the site.
This initial research identified for the first time the most pressing issues needing to be addressed in the prevention of further deterioration and restoration of the château. While the initial work has saved Maulnes and created a tourist attraction, it will take many more years before the château and grounds are fully restored to their original, 16th-century condition.
Description
.JPG.webp)
The site
Maulnes is 25 km from Tonnerre, the main city of the region, and 15 km of the châteaus of Tanlay and Ancy-le-Franc.
It lies on the edge of a large plateau of farmland that was once covered with forests. The 18th-century Cassini map shows the château surrounded by a vast forest, in a clearing at the intersection of five forest paths. These paths allowed for ease of logging and hunting, and also created a view of the château. The château has three predictable streams of water, providing water to the premises.
The château is a complex of three buildings. The entrance was a semicircular common, only a portion of which still remains. Contiguous with the common was a covered porch which has completely disappeared over the years. Lastly was an open air fixed bridge leading from the covered porch to the pentagonal house.
.JPG.webp)
The commons and the gallery
The commons was a semicircular building surrounding the courtyard, with one floor and an attic. The original Philibert Delorme structure was built around 1570–1572, but was replaced between 1662 and 1674 by a traditional frame. It had likely had undergone additional changes since then to adapt for industrial use at the time of the glassworks industry. A 1942 map shows the commons completely intact. Today, half of the structure is missing. The structure was dismantled in 2000-2001 for restoration work, but has
since been restored and now serve as public reception venue and exhibition hall.
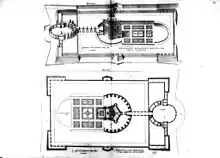
The extant entrance hallway was built in the center of the gallery and was centerpiece of the commons. The plans of Du Cerceau shows a floored gallery with five arches leading to an open-air fixed bridge supported by four columns and a moveable gateway. From the bridge over the moat was then the north tower of the pentagonal house.
The pentagonal house

The pentagonal house was built with five equal sides of about 17 m surrounding a hollow cylinder shaped well. Adjacent to the central space is a large spiral staircase which connects all five levels and the terrace at the top. Each pentagonal corner has a tower. Three of the towers have a staircase, probably intended for servants, allowing the central staircase to be reserved for the owners and their guests. Four towers are incorporated into the pentagonal form; while the fifth, the north tower, was added after the finished building, perhaps for reasons of safety from renewed war.
The building has an axis of symmetry that passes through the north tower and through the middle of the south facade.
Throughout the home, there are 21 fireplaces, which was not unusual given the harsh winters on the Maulnes plateau. On the roof, the five chimneys act to support the central terrace.

The well
The walls of the well contains several large windows arranged regularly. It was possible to draw water from the well to every floor, and there is evidence of wear due to the ropes in several locations, but especially on the third floor.

First and second floors
Due to the natural slope of the terrain, the first floor on the north side is buried while on the south side it is exposed. A diverted water source feeds the bowl, which in turn connects to the base of the interior well. The overflow of the bowl, as well as two other water sources, flowed into a basin or nymphaeum, partly inside and partly outside. These two floors included areas that could serve as storage areas, basements and cellars.
Third floor
The main entrance and vestibule of the pentagonal house is on the north side of the third floor. Research on this level has discovered evidence of a bathing room containing an oven, a boiler room and hypocaust (heated floor). These areas were accessible by a staircase from one of the main bedrooms of the upper floor. In the bathroom are remnants of a mural painted with an oil paint on mortar. The surviving traces show a forest backdrop and several female figures, possibly a representation of the legend of Diana.
.JPG.webp)
Fourth floor
This level was the main floor of activity, recognizable by the greater ceiling heights and two Doric columns that adorn it. From the description of Androuet du Cerceau, ceilings of this floor were quite remarkable, especially the enrayure-style box struts that are aligned diagonally with the room walls. A small room, identified as a washroom, is connected to the main bedroom. A water discharge, through the window sill, suggests a bathtub was once present.
The terrace
At the top of the château is a terrace surrounded by five chimney stacks, forming belvedere with a room for a roof lantern in the center. This lantern would have provided shelter from rain and would allow natural light to enter the central well below. It was later covered by a pyramidal roof, but this was removed in the twentieth century.

The facades
The main building was designed to be viewed primarily from a north–south angle. The five facades differ from each other, however, they all share three elements: an ashlar roof base, floors and an attic. The two north facades, situated on either side of the entry turret, combine and form an assembly; while the south facade and two towers that flank form another. The south facade opens to the garden and features a nymphaeum in the lower part.
The ashlar roof base was made up of a cornice with supporting corbels, the design of which were of alternating dog heads and lion heads, reflecting a hunting theme. Photographs from 1942, show that three dogs' heads were still in place at that time. This decoration has subsequently been reconstructed on the northeast and northwest facades. With the exception of heads, the facades appear very simple, which was uncommon at the time. However, their layout is well organized and more complex than it first appears. For example, there was a gradation of materials used; rustic stone for nymphée, smooth cut stones for the roof base, plaster cornices and protruding, stepped cornices floors.
Stone selection
The small rubble, used for interior wall siding, came from astartes limestone deposits located a few hundred meters from the château.
The majority of stones belong to the same geological layer of soft, chalky white limestone of Tonnerre. It was used indoors as well as for the frame of the well. Another similar facies, though less chalky and more hard, was used for the exterior walls.
A reddish stone was used in the masonry of the château, especially near the nymphaeum. It may have come from Indian bead limestone quarries located in the nearby communes of Massangis and Coutarnoux, near Avallon.
.JPG.webp)
The exterior
.JPG.webp)
The garden
From the first construction, the whole future garden area was cleared and pickled. Then the walls closing and walls dry moat were built. Closing the walls, including the most distant part of the château is in a semicircle, surrounded by a hedge and a grass glaze. The original plan seems to have planned the construction of a large outer wall with bastions, which was not realized. On the mode of "palazzo in fortezza" Italian (a palace in a fortress), it was probably to protect themselves from common disorders in these times of civil war.
The nymphaeum
By reflecting the image of the château, the nymphaeum acts as a unifying element between the gardens and château. The vault of the basin is made of segments of alternating color. The exterior as well as the lintels of Level 1, is rusticated. In original plans of Du Cerceau, it is shown surrounded by bleachers forming a small theater. Yet the archaeological excavations suggest this was never present and the original plan for the nymphaeum was simplified. The current theories suggest a terrace wall separated the enclosed basin from the rest of the garden, interrupted by an access staircase. The plan of Du Cerceau could have corresponded to a project of later development that never came to fruition due to the abandonment of the site or the death of Antoine de Crussol. The nymphaeum was completely restored in 2012.[3]
See also
Bibliography
- Babelon, Jean-Pierre (1989). Châteaux de France au siècle de la Renaissance (in French). Paris: Flammarion/Picard. pp. 547–549, 799. ISBN 2-08-012062-X.
- Barnoud, Paul (2011). Le château de Maulnes (in French). Paris: Société Française d'Archéologie. ISBN 978-2-901837-39-8.
- Chatenet, Monique (2004). Maulnes: archéologie d'un château de la Renaissance (in French). Paris: Picard. ISBN 2-7084-0725-2.
- This french language publication is the result of archaeological research and historical investigations for four years by the multidisciplinary team commissioned by the General Council of the Yonne. It forms the major source of this article.
- de Cossé-Brissac, Philippe (1947). Châteaux de France disparus (in French). Paris: Éditions Tel.
- Dauphin, Jean-Luc (2011). Maulnes en Tonnerrois, rêve de pierre de la Renaissance (in French). Paris: Éditions du Palais. ISBN 978-2-35251-020-8.
- Henrion, Fabrice (2001). "L'appartement des bains du château de Maulnes: analyse archéologique des sols et des élévations". Bulletin Monumental (in French). 159 (1): 77–89. doi:10.3406/bulmo.2001.970.
- Gandsart, Hervé (November 1991). "L'Énigme de Maulne". Connaissance des arts (in French). No. 477. Paris: Société française de promotion artistique. pp. 100–107.
- Le Château de Meaulnes en Bourgogne, catalogue d'exposition édition bilingue allemand et français, auteur (collectif) Institut d'Histoire de l'Architecture Aix-la Chapelle /Aachen, 1999 Aachen, 53 pages. Ce document rassemble les plans de niveaux et les élévations de façades avant restauration effectués par des étudiants d'Aix-la-Chapelle. Ces dessins sont d'une précision remarquable, sauf l'axonométrie de l'escalier qui est fausse.
- "Maulnes appartenant à Louise de Clermont-Tallart" étude critique et enquête[4] sur les recherches et travaux en cours. Auteur Alain Oudin architecte-urbaniste, Enseigne-des-Oudin, Paris 2009.
References
- Base Mérimée: PA00113666, Ministère français de la Culture. (in French)
- Jacques Androuet Hoop published the first volume of the "Plus Excellents Bastiments de France"
- "Le château de Maulnes : saison 2016". 25 March 2014. Archived from the original on 13 May 2014. Retrieved 29 October 2016.
- L'hypothèse est que 3 projets se succèdent 1)"manifeste maniériste" de Serlio? vers 1550? pour les Bellay 2)sur la base du même "parti savant" une construction "hédoniste" pour les Crussol de 1566 à 1573 par Primatice et/ou Delorme 3)Par Louise veuve une seconde fois, qui ne reviendra plus à Maulnes bien qu'elle vive jusqu'en 1596, des modifications banalisantes entre 1573 et 1575-76 pour une "occupation bourgeoise", et paradoxalement, ceci au moment précis de la publication prestigieuse de Jacques Androuet du Cerceau en 1576.
External links
- Official site (French only)
- Les Cahiers de Maulnes, a French-language magazine published by the General Council of the Yonne.