Chiemgau
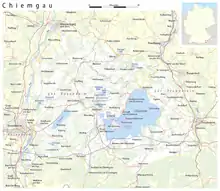
Chiemgau (German pronunciation: [ˈkiːmɡaʊ]) is the common name of a geographic area in Upper Bavaria. It refers to the foothills of the Alps between the rivers Inn and Traun, with the Chiemsee at its center. The political districts that contain the Chiemgau are Rosenheim and Traunstein. Wendelstein is the name of a famous mountain close by but not strictly in the Chiemgau.

Explanation of the name
The name Chiemgau and Chiemsee together with the place name Chieming allegedly go back to the Old High German personal name Chiemo (7th/8th century). At the end of the 8th century the name Chiemgau appeared for the first time in documents as Chimigaoe but it stood at that time for a smaller area around the village of Chieming.
History
From the New Stone Age to the Bronze and Iron Ages humans have left their traces in the Chiemgau. After that this region was settled by the Celts and later by the Romans. The Romans settled mainly near the river Alz and made a crossing for their Roman road which goes from Salzburg to Augsburg at Seebruck (Bedaium). At that time the Chiemgau was on the outskirts of the Roman province of 'Noricum'. The Chiemgau was for a long time closely connected with the Bavarian dukes and also the prince-bishops of Salzburg.
After the secularisation of 1803, the whole Chiemgau district became part of Bavaria.
The Chiemgau is a source of wood, iron and salt. The production of salt, which existed from 1619 till 1912, had a big cultural and economical influence on the Chiemgau.
The Chiemgau has traditionally been horse breeding country, especially workhorses.
Nature and geography
The ice-age, which took place 15000 years ago, formed the foothills of the Alps and the morainic landscape. For this reason the Chiemgau is a hilly countryside with numerous grasslands, forests and fens; additional there are plenty of lakes of which the biggest one is the Chiemsee. The biggest mountains are almost 2000m high.
Notable residents
- Karl Streibel (1903–1986), German Nazi SS concentration camp commandant