Chukotko-Kamchatkan–Amuric languages
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan–Amuric languages form a hypothetical language family including Nivkh and Chukotko-Kamchatkan. A relationship between Chukotko-Kamchatkan and Nivkh was proposed by Michael Fortescue. He theorized that their common ancestor might have been spoken around 4000 years ago.[1] However Glottolog says that the evidence is insufficient to conclude a genealogical relationship between Nivkh and Chukotko-Kamchatkan.[2]
| Chukotko-Kamchatkan–Amuric | |
|---|---|
| (hypothetical) | |
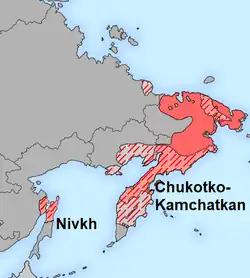
| Geographic distribution | Northeast Asia |
| Linguistic classification | Proposed language family |
| Subdivisions | |
| Glottolog | None |
 | |
Evidence
Phonological
Proposed sound correspondences[1]
| Nivkh | CK |
|---|---|
| p, t, c, k, q | p’, t’, c’, k’, q’ |
| p’, t’, c’, k’, q’ | v, r/z, γ, R |
| m, n, n, ŋ | m, n, n’, ŋ |
| w, j | w, j |
| ə | æ |
Some cognates which include a sound change of Nivkh /ə/ and CK /æ/ are: t’əkə ‘edge of sleeping platform’ and CK tæγən 'near the edge of'' and Nivkh ərŋ 'mout of a river' and CK ær 'flow out'.
Lexical
Proposed Nivkh-Chukotko-Kamchatkan cognates[3]
| Nivkh | CK |
|---|---|
| aui 'mouth' | æw 'get a hole' |
| kama 'run' | kame 'move around' |
| juty 'pour' | jit 'drip' |
| poju 'smoke' (verb) | pujæ 'cook on hot stones in pit' |
| t'am 'stay calm' | təmɣə 'stay still, calm' |
| uige 'no' | ujŋæ 'no' |
Morphological
Chukotko-Kamchatkan and Nivkh have dual/plural distinction, however it has been lost in Chukchi.
Chukotko-Kamchatkan also has a "singulative" ending, and traces of a singulative ending in Nivkh might be seen.
References
- Fortescue, Michael (2011). "The relationship of Nivkh to Chukotko-Kamchatkan revisited". Lingua. 121 (8): 1359–1376. doi:10.1016/j.lingua.2011.03.001.
- "Glottolog 4.3 - Amur Nivkh". glottolog.org.
- Fortescue, Michael (1998). Language Relations across Bering Strait. London: Cassell & Co.
.svg.png.webp)