Coastal black-handed titi monkey
The coastal black-handed titi monkey (Callicebus melanochir) is a species of titi, a type of New World monkey, endemic to Brazil.[3]
| Coastal black-handed titi[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Coastal black-handed titi (Callicebus melanochir) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Pitheciidae |
| Genus: | Callicebus |
| Species: | C. melanochir |
| Binomial name | |
| Callicebus melanochir (Wied-Neuwied, 1820) | |
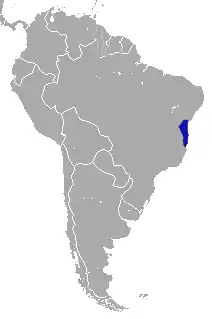 | |
| Coastal black-handed titi range | |
Description
Coastal black-handed titis are relatively small primates with fluffy fur, a long, bushy tail and a small, roundish head. Like atlantic titis, they can reach a head trunk length of over 40 centimetres and a weight of up to 1.6 kilograms. Their dense fur is predominantly grey or grey-brown in colour, the head and paws are black. The long tail is the same colour as the torso, as with all jumping monkeys it cannot be used as a prehensile tail.
Distribution and habitat
Coastal black-handed titis are found on the Brazilian Atlantic coast, their range includes the south of Bahia and the north of Espírito Santo. Their habitat is coastal forest.
Behavioral ecology
Not much is known about the lifestyle of the coastal black-handed titis, but it is probably the similar to that of the atlantic titi. They are diurnal tree dwellers that move around on all fours or jumping. A male and a female, who stay together all their lives, form a family group with their offspring. These groups live in fixed territories, which they mark with songs and defend aggressively if necessary. They feed mainly on fruits and to a lesser extent on seeds and leaves. The fathers participate intensively in the rearing of the young, they carry the young around and only leave it to the mother to suckle.
Conservation
The habitat of the Southern Bahia Jumping Monkey is located in one of the most densely populated regions of Brazil, and its range is correspondingly reduced and fragmented. The main threat is the ongoing habitat destruction; the IUCN lists the species as "vulnerable".
Literature
- Thomas Geissmann: Vergleichende Primatologie. Springer-Verlag, Berlin u. a. 2003, ISBN 3-540-43645-6.
- Marc G. M. van Roosmalen, Tomas van Roosmalen und Russell A. Mittermeier: A Taxonomic Review of the Titi Monkeys, Genus „Callicebus“ Thomas 1903, with the Description of two New Species: „Callicebus bernhardi“ and „Callicebus stepehnnashi“, from Brazilian Amazonia. In: Neotropical Primates. 10, ISSN 1413-4705, 2002, S. 1–52, PDF.
- Don E. Wilson, DeeAnn M. Reeder (Hrsg.): Mammal Species of the World. A taxonomic and geographic Reference. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore MD 2005, ISBN 0-8018-8221-4.
Weblinks
References
- Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 144. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- Printes, R.C.; Jerusalinsky, L.; de Melo, F.R.; Mittermeier, R.A. (2020). "Callicebus melanochir". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T39930A17975106. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T39930A17975106.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- Costa-Araújo, Rodrigo; Luis Regolin, André; Martello, Felipe; Pedro Souza-Alves, João; Hrbek, Tomas; Cezar Ribeiro, Milton (2021-04-26). "Occurrence and conservation of the Vulnerable titi monkey Callicebus melanochir in fragmented landscapes of the Atlantic Forest hotspot". Oryx. 55 (6): 916–923. doi:10.1017/S0030605319001522. ISSN 0030-6053.
