Cochleoid
In geometry, a cochleoid is a snail-shaped curve similar to a strophoid which can be represented by the polar equation
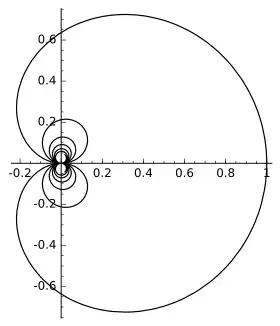
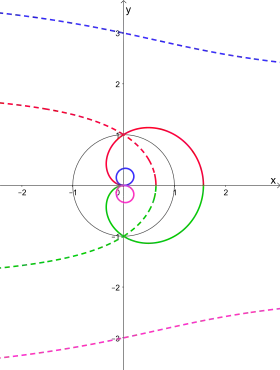
cochleoid (solid) and its polar inverse (dashed)
or the parametric equations
The cochleoid is the inverse curve of Hippias' quadratrix.[1]
Notes
- Heinrich Wieleitner: Spezielle Ebene Kurven. Göschen, Leipzig, 1908, pp. 256-259 (German)
References
- J. Dennis Lawrence (1972). A catalog of special plane curves. Dover Publications. p. 192. ISBN 0-486-60288-5.
- Cochleoid in the Encyclopedia of Mathematics
- Liliana Luca, Iulian Popescu: A Special Spiral: The Cochleoid. Fiabilitate si Durabilitate - Fiability & Durability no 1(7)/ 2011, Editura "Academica Brâncuşi" , Târgu Jiu, ISSN 1844-640X
- Roscoe Woods: The Cochlioid. The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 31, No. 5 (May, 1924), pp. 222–227 (JSTOR)
- Howard Eves: A Graphometer. The Mathematics Teacher, Vol. 41, No. 7 (November 1948), pp. 311-313 (JSTOR)
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cochleoid.
- cochleoid at 2dcurves.com
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Cochleoid". MathWorld.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.