Coelenteramine
Coelenteramine is a metabolic product of the bioluminescent reactions in organisms that utilize coelenterazine. It was first isolated from Aequorea victoria along with coelenteramide after coelenterates were stimulated to emit light.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
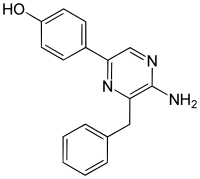
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Benzyl-5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyrazin-2-amine | |
| Other names
Coelenteramine, 2-Amino-3-benzyl-5-(p-hydroxyphenyl)pyrazine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H15N3O | |
| Molar mass | 277.327 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Shimomura O, Johnson FH (1975). "Chemical Nature of Bioluminescence Systems in Coelenterates". PNAS USA. 72 (4): 1546–1549. doi:10.1073/pnas.72.4.1546. PMC 432574. PMID 236561.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.