Collicular artery
The collicular artery or quadrigeminal artery arises from the posterior cerebral artery. This small artery supplies portions of the midbrain,[1] especially the superior colliculus, inferior colliculus, and tectum.
| Collicular artery | |
|---|---|
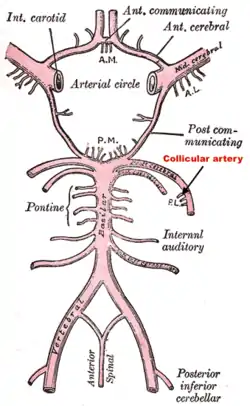 The collicular artery is the first artery that arises from the posterior cerebral artery just distal to the bifurcation of the basilar artery. | |
| Details | |
| Supplies | Superior colliculus and Inferior colliculus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteria collicularis |
| TA98 | A12.2.07.087 |
| FMA | 50625 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structure
The collicular artery originates from P1 segment of the posterior cerebral artery near the side of interpeduncular fossa.[2] It arises just distal to the bifurcation of the basilar artery. It runs posteriorly along the cerebral peduncle passing the crural and ambient cisterns. It then gives off branches to supply quadrigeminal plate and the adjacent structures in the midbrain. The origin of this artery is proximal to the origin of medial and lateral posterior choroidal branch of the posterior cerebral artery. The main collicular artery also gives branch to an accessory collicular artery.
Branches
- Anterior branches
Anteromedial branches are rare but sometimes observed to contribute as part of the interpeduncular fossa's lateral rami of the intermediate pedicle. Anterolateral branches are abundant branching from both main and accessory collicular arteries. They only exist on the lower part of celebral crus.[2]
- Lateral branches
These lateral branches are found near lateral part of celebral crus arising from both main and accessory collicular arteries.[2]
- Posterior branches
These branches originate from the terminal branch of the collicular artery.[2]
Function
This small artery supplies the superior colliculus, inferior colliculus, and tectum of midbrain.
References
- Tatu, Laurent; Moulin, Thierry; Bogousslavsky, Julien; Duvernoy, Henri (1996-11-01). "Arterial territories of human brain Brainstem and cerebellum". Neurology. 47 (5): 1125–1135. doi:10.1212/WNL.47.5.1125. ISSN 0028-3878. PMID 8909417.
- Duvernoy, Henri M. (2013). Human Brain Stem Vessels: Including the Pineal Gland and Information on Brain Stem Infarction. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 47. ISBN 9783662078136.