Corisco
Corisco, Mandj, or Mandyi,[1] is a small island of Equatorial Guinea, located 29 km (18 mi) southwest of the Río Muni estuary that defines the border with Gabon. Corisco, whose name derives from the Portuguese word for lightning, has an area of 14 km2 (5 sq mi), and its highest point is 35 m (115 ft) above sea level. The most important settlement on the island is Gobe.
| Disputed island | |
|---|---|
 | |
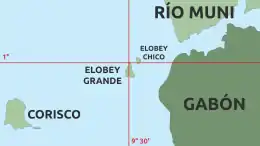 Corisco Island and Elobey Islands | |
 Corisco | |
| Geography | |
| Coordinates | 0°54′54″N 9°19′12″E |
| Area | 14 km2 (5.4 sq mi) |
| Length | 6 km (3.7 mi) |
| Width | 5 km (3.1 mi) |
| Highest point | 35 m |
| Administration | |
| Litoral | |
| Insular Region | |
| Claimed by | |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
History
During the Iron Age (50 BC - 1400 AD) and before the arrival of the Portuguese, the island was densely settled. The most important evidence of human occupation comes from the area of Nandá, near the eastern coast, where dozens of prehistoric burials have been excavated.[2] These burials belong to two different periods: Early Iron Age (50 BC - 450 AD) and Middle Iron Age (1000-1150 AD). During the first period, the islanders deposited bundles of human bones and iron implements (axes, bracelets, spears, spoons, iron currency) in shallow pits dug in the sand. During the second period, tombs have been documented where the corpses (not preserved) lay surrounded by pots, probably containing food and alcoholic beverages. The deceased were interred with their adornments (collars, bracelets and anklets) and a few personal possessions (knives and adzes).
When Portuguese sailors arrived in the Mino Estuary in 1471, they noted that the islands in the area were mainly unpopulated. They named Corisco after 'lightning', due to the gales they experienced around the island.[3] After more than three centuries of abandonment, when it was sporadically visited by European sailors, Corisco was settled by the Benga people.[3] They arrived during the second half of the 18th century attracted by the prospects of trade with the Europeans. The island was later acquired by Spain in 1843, as a result of an arrangement made by Juan José Lerena y Barry with Benga king Bonkoro I. Bonkoro I died in 1846 and was succeeded by his son Bonkoro II, but due to rivalries on the island, Bonkoro II moved to São Tomé, and Munga I ruled in Corisco 1848 to 1858, his son Munga II taking over, and meeting the explorer Manuel Iradier in the 1870s.
In general, the Spanish paid little attention to Corisco. In the early part of the 20th century it was part of the administration of Elobey, Annobon, and Corisco, and postage stamps were issued under that name. It became an integral part of Equatorial Guinea upon independence.
Corisco and the surrounding waters of Corisco Bay have become of interest in recent years for their oil prospects. A consortium of Elf Aquitaine and Petrogab began prospecting in 1981. The area is disputed with Gabon because of the perceived value of the oil. In February 2003, Gabonese Defence Minister Ali-Ben Bongo Ondimba visited the islands and re-stated Gabon's claim to them.[4]
See also
References
- "Isla de Corsico | Marine World Database". 2015-05-11. Archived from the original on 2015-05-11. Retrieved 2022-08-01.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - Ayán Vila, Xurxo; González-Ruibal, Alfredo; García-Rodríguez, Sonia; Otero Vilariño, Carlos; Picornell Gelabert, Llorenç; Sánchez-Elipe Lorente, Manuel; Trigo, Mario; Bayre, Francesca; Valenciano Mañé, Alba; Porto Tenreiro, Yolanda (June 15, 2011). "Arqueología en el Estuario del Muni (Guinea Ecuatorial)". digital.csic.es. doi:10.13039/501100003767. Retrieved November 15, 2022 – via digital.csic.es.
- Mark P. Leone; Jocelyn E. Knauf (27 May 2015). Historical Archaeologies of Capitalism. Springer. p. 430. ISBN 978-3-319-12760-6.
- "Gabon-Equatorial Guinea: UN mediates dispute over Corisco Bay islands", IRIN, January 23, 2004.
Further reading
- X. Ayán Vila et al., Arqueología en el Estuario del Muni (Guinea Ecuatorial). Revista de Arqueología, 362: 24–33.
- Manuel Iradier Bulfi (1878). Fragmentos de un diario de viajes de exploración en la zona de Corisco. Fortanet. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- Mary Henrietta Kingsley; Albert Carl Ludwig Gotthilf Günther; William Forsell Kirby (1897). Travels in West Africa: Congo Francais, Corisco and Cameroons. Macmillan. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- Max Liniger-Goumaz, Small is not always beautiful: The Story of Equatorial Guinea (1989, ISBN 0-389-20861-2) p. 7.
- José Muñoz y Gaviria (1870). Crónica de las Islas de Fernando Póo, Corisco y Annobon. Rubio. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- Francisco Salvadó y Cos (1891). Colección de apuntes preliminares sobre la lengua benga: ó sea, Intrucción a una gramática de este idióma que se habla en la isla de Corisco, pueblos de su bahía é islas adyacentes. Impr. de A. Pérez Cubrull. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
External links
![]() Media related to Corisco at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Corisco at Wikimedia Commons