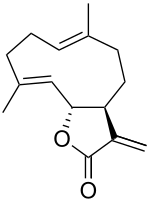
Costunolide
(+)-Costunolide is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene lactone, first isolated in Saussurea costus roots in 1960.[1] It is also found in lettuce.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3aS,6E,10E,11aR)-6,10-Dimethyl-3-methylidene-3a,4,5,8,9,11a-hexahydrocyclodeca[b]furan-2(3H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.663 |
| MeSH | (+)-Costunolide |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H20O2 | |
| Molar mass | 232.323 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Synthesis
It is synthesized through the mevalonate pathway, seen in Figure 1. The synthesis begins with the cyclization of compound 1, farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), which is mediated by a sesquiterpene cyclase, (+)-germacrene A synthase, to form compound 2, (+)-germacryl cation.[1] Inside this same enzyme, a proton is lost to form 3, (+)-germacrene A.[2] The isoprenyl side chain of (+)-germacrene A is then hydroxylated by (+)-germacrene A hydroxylase, which is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, to form 4.[1] NAD(P)+ dependent hydrogenase(s) then oxidize 4, germacra-1(10),4,11(13)-trien-12-ol, through the intermediate 5, germacra-1(10),4,11(13)-trien-12-al to form compound 6, germacrene acid. The cytochrome P450 enzyme, (+)-costunolide synthase, which is a NADPH and O2 dependent enzyme, then oxidizes germacrene acid to give the alcohol intermediate, 7, which then cyclizes to form the lactone 8, (+)-costunolide.[3]

Figure 1. Biosynthesis of (+)-Costunolide.[2]
References
- Kraker, J.; Franssen, M.; Dalm, M.; Groot, A.; Bouwmeester, H. (April 2001). "Biosynthesis of Germacrene A Carboxylic Acid in Chicory Roots. Demonstration of a Cytochrome P450 (+)-Germacrene A Hydroxylase and NADP+-Dependent Sesquiterpenoid Dehydrogenase(s) Involved in Sesquiterpene Lactone Biosynthesis". Plant Physiology. 125 (4): 1930–1940. doi:10.1104/pp.125.4.1930. PMC 88848. PMID 11299372.
- Dewick, Paul M. (2009). Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach. West Sussex, United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. p. 214.
- Kraker, J.; Franssen, M.; Joerink, M.; Groot, A.; Bouwmeester, H. (April 2002). "Biosynthesis of Costunolide, Dihydrocostunolide, and Leucodin. Demonstration of Cytochrome P450-Catalyzed Formation of the Lactone Ring Present in Sesquiterpene Lactones of Chicory". Plant Physiology. 129: 257–258. doi:10.1104/pp.010957. PMC 155889. PMID 12011356.