Coumachlor
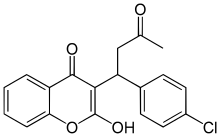
Coumachlor is a first generation anticoagulant rodenticide which blocks formation of prothrombin and inhibits blood coagulation causing death by internal haemorrhage.[1][2] The chemical can be absorbed through the skin.[3] The symptoms of human contact can be nosebleeds, bleeding gums, bloody urine, extensive bruising in the absence of injury, fatigue, shortness of breath (dyspnea) on exertion. The human consumption or inhalation of compound can also cause fluid in lungs (pulmonary edema).
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-oxobutyl]-2-hydroxychromen-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.254 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H15ClO4 | |
| Molar mass | 342.77 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/ProductDetail.do?D7=0&N5=SEARCH_CONCAT_PNO%7CBRAND_KEY&N4=189219%7CALDRICH&N25=0&QS=ON&F=SPEC Archived January 19, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-26. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Health Content A-Z".
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.