Counties of Sweden
The counties of Sweden (Swedish: Sveriges län) are the top-level geographic subdivisions of Sweden. Sweden is today divided into 21 counties; however, the number of counties has varied over time, due to territorial gains/losses and to divisions and/or mergers of existing counties. This level of administrative unit was first established in the 1634 Instrument of Government on Lord Chancellor Count Axel Oxenstierna's initiative, and superseded the historical provinces of Sweden (Swedish: landskap) in order to introduce a more efficient administration of the realm. At that time, they were what the translation of län into English literally means: fiefdoms. The county borders often follow the provincial borders, but the Crown often chose to make slight relocations to suit its purposes.
| Counties of Sweden Sveriges län (Swedish) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Sweden |
| Number | 21 |
| Populations | Least: Gotland, 59,686 Most: Stockholm, 2,377,081 |
| Areas | Smallest: Blekinge, 2946.4 km2 Largest: Norrbotten, 98244.8 km2 |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
.svg.png.webp) |
|---|
| Administrative divisions of Sweden |
|---|
.svg.png.webp) |
| Counties of Sweden |
| Municipalities of Sweden |
| List of municipalities |
| Other divisions |
|
|
|
In every county there is a county administrative board (länsstyrelse) headed by a governor (landshövding), appointed by the government, as well as a separate regional council (region). In the county of Gotland however, the county's only municipality has adopted regional responsibilities.
The aims of the county administrative board are to supervise local state administration (that is not otherwise assigned to other government agencies), and to coordinate political goals with the central government. The regional council is the elected regional political assembly that oversees the municipal affairs of the county, primarily in regard to public healthcare, public transport, and culture.
Beginning in the 2000s, many major government agencies have reorganised from a countybased subdivisional structure into larger geographical or functional areas. This include the Swedish Tax Agency (1 January 2004), the Swedish Social Insurance Agency (1 January 2005), the Swedish Public Employment Service (1 January 2008), and the Swedish Police Authority (1 January 2015).
List of counties
| ISO | NUTS | CoA | County (Län) | Administrative centre | Governor | Area (km2) |
Pop. (2019)[1] |
Den. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE-AB | SE110 | Stockholm | Anna Kinberg Batra | 6,519.3 | 2,377,081 | 360 | ||
| SE-C | SE121 | Uppsala | Göran Enander | 8,207.2 | 383,713 | 45 | ||
| SE-D | SE122 | Nyköping | Beatrice Ask | 6,102.3 | 297,540 | 52 | ||
| SE-E | SE123 | Linköping | Carl Fredrik Graf | 10,602.0 | 465,495 | 43 | ||
| SE-F | SE211 | Jönköping | Helena Jonsson | 10,495.1 | 363,599 | 34 | ||
| SE-G | SE212 | Växjö | Maria Arnholm | 8,466.0 | 201,469 | 23 | ||
| SE-H | SE213 | Kalmar | Peter Sandwall | 11,217.8 | 245,446 | 22 | ||
| SE-I | SE214 | Visby | Anders Flanking | 3,151.4 | 59,686 | 19 | ||
| SE-K | SE221 | Karlskrona | Ulrica Messing | 2,946.4 | 159,606 | 52 | ||
| SE-M | SE224 | Malmö, Kristianstad | Anneli Hulthén | 11,034.5 | 1,377,827 | 120 | ||
| SE-N | SE231 | Halmstad | Brittis Benzler | 5,460.7 | 333,848 | 59 | ||
| SE-O | SE232 | Gothenburg, Vänersborg | Lisbeth Schultze (acting) | 23,948.8 | 1,725,881 | 68 | ||
| SE-S | SE311 | Karlstad | Georg Andrén | 17,591.0 | 282,414 | 16 | ||
| SE-T | SE124 | Örebro | Maria Larsson | 8,545.6 | 304,805 | 35 | ||
| SE-U | SE125 | Västerås | Ulrica Gradin (acting) | 5,145.8 | 275,845 | 37 | ||
| SE-W | SE312 | Falun | Camilla Fagerberg Littorin (acting) | 28,188.8 | 287,966 | 10 | ||
| SE-X | SE313 | Gävle | Per Bill | 18,198.9 | 287,382 | 16 | ||
| SE-Y | SE321 | Härnösand | Berit Högman | 21,683.8 | 245,347 | 11 | ||
| SE-Z | SE322 | Östersund | Marita Ljung | 49,341.2 | 130,810 | 3.4 | ||
| SE-AC | SE331 | Umeå | Helene Hellmark Knutsson | 55,186.2 | 271,736 | 4.9 | ||
| SE-BD | SE332 | Luleå | Lotta Finstorp | 98,244.8 | 250,093 | 2.6 |
Map
With county codes, which were official until 1974.
|
 Counties of Sweden |
 Comparison with the provinces of Sweden
Bold lines represent county borders, colors represent provinces.
|
Each county region contains a number of municipalities (kommuner), the existence of which is partly at the discretion of the central government. Since 2004 their number has been 290, thus an average of 13.8 municipalities per county.
Until 1968, the City of Stockholm had its own "county code" A, which is still used interchangeably with AB in some contexts, and County of Stockholm had county code B. L was for Kristianstad County and M was for Malmöhus County but since they were merged to form Skåne County, M is usually used. O used to stand for Gothenburg and Bohus County but has been used for Västra Götaland County since it was merged with Skaraborg County (R) and Älvsborg County (P).
History
Older subdivisions
Sweden's provinces, or landskap, and the "lands", or landsdelar, lack political importance today but are common denominations culturally and historically. The provinces had their own laws and justice systems and could have large cultural and religious differences. The province of Småland (literally small land) historically was several provinces with its own laws. Here burial tradition in the era before the Viking Age could differ significantly from province to province. The province of Norrbotten is a relatively recent creation; it was part of Västerbotten which extended all the way to Österbotten into today's Finland before 1809. Finnish and Swedish Lappland was also one province until 1809.
Historically, the provinces were grouped in three lands: Götaland, being southern and western Sweden; Svealand being eastern and south-eastern, and Norrland being the entire northern half. The names of the first two refer to ancient tribes, and the third is a geographical reference. They are still commonly used as geographical references. The boundaries have changed over time, with the most significant in 1658 (the cession of provinces from Denmark-Norway to Sweden) and 1812 (due to the loss of Finland to Russia in 1809). In 1812 some provinces were moved from Götaland to Svealand.
Finland
After the Finnish War, Sweden was forced to cede the counties in Finland to Russia following the Treaty of Fredrikshamn in (1809). However, the counties were upheld in Finland until a reform in 1997. They are still in use in Sweden, 370 years later.
The counties in Finland established in 1634 were: Turku and Pori County, Nyland and Tavastehus County, Viborg and Nyslott County, Ostrobothnia County and Kexholm County. Over time the number of subdivisions in Finland increased to twelve, until a reorganization in 1997 reduced their number to six provinces, while keeping the administrative model intact. The counties in Finland were abolished in 2010.
Abolished counties
Abolished counties in current-day Sweden proper were:
- Skaraborg County + Gothenburg and Bohus County + Älvsborg County (merged as Västra Götaland County in 1998)
- Kopparberg County (became Dalarna County in 1997)
- Malmöhus County + Kristianstad County (merged as Skåne County in 1997)
- Norrland County (in 1645 divided into Västerbotten County, Hudiksvall County and Härnösand County)
- Nyköping County, Gripsholm County and Eskilstunahus County (united in 1683 to become Södermanland County)
- Närke County (became Örebro County)
- Härnösand County (1645–1654, formed Västernorrland County)
- Hudiksvall County (1645–1654, formed Gävleborg County)
- Office of the Governor of Stockholm (1634–1967, united with Stockholm County)
- Svartsjö County (1786–1809, united with Stockholm County)
- Öland County (1819–1826, united with Kalmar County)
Counties in Swedish-ruled Finland were:
- Turku and Pori County (1634–1809)
- Nyland and Tavastehus County (1634–1809)
- Ostrobothnia County (1634–1775)
- Viborg and Nyslott County (1634–1721)
- Kexholm County (1634–1721)
- Kymmenegård and Nyslott County (1721–1747)
- Savolax and Kymmenegård County (1747–1775)
- Vasa County (1775–1809)
- Oulu County (1775–1809)
- Kymmenegård County (1775–1809)
- Savolax and Karelia County (1775–1809)
Proposed regions

Under the aegis of the Swedish government, Ansvarskommittén has been investigating the possibilities of merging the current 21 counties into 6 to 9 larger regions. These proposals are from their final report, delivered in 2007:[2]
A model for this comes from the merger of some counties into Skåne County and Västra Götaland County in 1997 and 1998, respectively, which is now considered a success.
The counties are discussing the proposal. An obstacle is that Stockholm County does not want to merge with any other county, while its neighbours want to merge with Stockholm. After this discussion the following proposal has in 2016 emerged:
- Norrbotten, Västerbotten, Västernorrland and Jämtland county
- Dalarna, Gävleborgs, Södermanlands, Uppsala, Västmanland and Örebro county
- Östergötland, Jönköping, Kalmar and Kronoberg county
- Gotland and Stockholm county
- Halland, Värmland and Västra Götaland county
- Blekinge and Skåne county
The main difference is that the proposed Bergslagen is divided to other counties, and Stockholm is on its own (plus the small Gotland which has air connections to Stockholm)
Riksområden
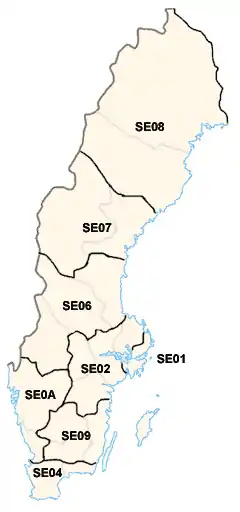
The counties in Sweden correspond to the third level of division in the European Union's system of Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics. For the purpose of creating regions corresponding to the second level, counties have been grouped into eight Riksområden, or National Areas: Stockholm, East Middle Sweden, North Middle Sweden, Middle Norrland, Upper Norrland, Småland and the islands, West Sweden and South Sweden.
See also
References
- "Sweden: Major Municipalities". City Population. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- "Regional utveckling och regional samhällsorganisation". Government Offices of Sweden (in Swedish). 23 March 2007. SOU 2007:13.