Crataegus sanguinea
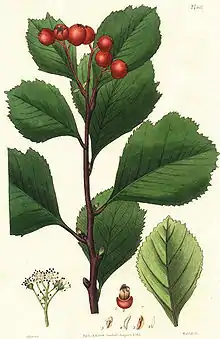
Crataegus sanguinea (common names redhaw hawthorn or Siberian hawthorn) is a species of hawthorn that is native to southern Siberia, Mongolia, and the extreme north of China. It is cultivated for its edible red berry-like fruit which actually is a pome. The fruit can be eaten raw or cooked. They can be used to make jam, jelly, and fruit preserves. They are also grown in gardens as ornamental plants. The flowers are small, white in color, and occur in clusters. The flowers give off a carrion smell.
| Crataegus sanguinea | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Rosaceae |
| Genus: | Crataegus |
| Section: | Crataegus sect. Sanguineae |
| Series: | Crataegus ser. Sanguineae |
| Species: | C. sanguinea |
| Binomial name | |
| Crataegus sanguinea | |
The world's largest living individual of this species can be found in Volunteer Park, Seattle, Washington.[1]
References
- Arthur Lee Jacobson (2001). "Trees of Volunteer Park".
External links
- Crataegus sanguinea information from Plants for a Future
![]() Media related to Crataegus sanguinea at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Crataegus sanguinea at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.