Critical transition
Critical transitions are abrupt shifts in the state of ecosystems, the climate, financial systems or other complex dynamical systems that may occur when changing conditions pass a critical or bifurcation point. As such, they are a particular type of regime shift. Recovery from such shifts may require more than a simple return to the conditions at which a transition occurred, a phenomenon called hysteresis.[1][2][3][4]
Early-warning signals and critical slowing down
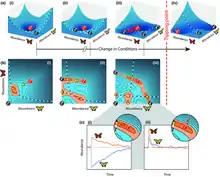


Significant efforts have been made to identify early-warning signals of critical transitions.[7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14] Systems approaching a bifurcation point show a characteristic behaviour called critical slowing down leading to an increasingly slow recovery from perturbations. This, in turn, may lead to an increase in (spatial or temporal) autocorrelation and variance, while variance spectra tend to lower frequencies,[8][11][12] and the 'direction of critical slowing down' in a system's state space may be indicative of a system's future state when delayed negative feedbacks leading to oscillatory or other complex dynamics are weak.[5] Researchers have explored early-warning signals in lakes, climate dynamics, the Amazon rainforest,[15] forests worldwide,[6] food webs, dry-land transitions and epilepsy attacks.[8]
Studies show that more than three-quarters of Amazon rainforest has been losing resilience since the early 2000s as measured by CSD[15] and that tropical, arid and temperate forests are substantially losing resilience.[6] It has been proposed that a loss of resilience in forests "can be detected from the increased temporal autocorrelation (TAC) in the state of the system, reflecting a decline in recovery rates due to the critical slowing down (CSD) of system processes that occur at thresholds".[6]
See also
References
- Scheffer, Marten; Carpenter, Steve; Foley, Jonathan A.; Folke, Carl; Walker, Brian (October 2001). "Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems". Nature. 413 (6856): 591–596. Bibcode:2001Natur.413..591S. doi:10.1038/35098000. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 11595939. S2CID 8001853.
- Scheffer, Marten (26 July 2009). Critical transitions in nature and society. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0691122045.
- Scheffer, Marten; Bascompte, Jordi; Brock, William A.; Brovkin, Victor; Carpenter, Stephen R.; Dakos, Vasilis; Held, Hermann; van Nes, Egbert H.; Rietkerk, Max; Sugihara, George (September 2009). "Early-warning signals for critical transitions". Nature. 461 (7260): 53–59. Bibcode:2009Natur.461...53S. doi:10.1038/nature08227. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 19727193. S2CID 4001553.
- Scheffer, Marten; Carpenter, Stephen R.; Lenton, Timothy M.; Bascompte, Jordi; Brock, William; Dakos, Vasilis; Koppel, Johan van de; Leemput, Ingrid A. van de; Levin, Simon A.; Nes, Egbert H. van; Pascual, Mercedes; Vandermeer, John (19 October 2012). "Anticipating Critical Transitions". Science. 338 (6105): 344–348. Bibcode:2012Sci...338..344S. doi:10.1126/science.1225244. hdl:11370/92048055-b183-4f26-9aea-e98caa7473ce. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 23087241. S2CID 4005516.
- Lever, J. Jelle; Leemput, Ingrid A.; Weinans, Els; Quax, Rick; Dakos, Vasilis; Nes, Egbert H.; Bascompte, Jordi; Scheffer, Marten (2020). "Foreseeing the future of mutualistic communities beyond collapse". Ecology Letters. 23 (1): 2–15. doi:10.1111/ele.13401. PMC 6916369. PMID 31707763.
- Forzieri, Giovanni; Dakos, Vasilis; McDowell, Nate G.; Ramdane, Alkama; Cescatti, Alessandro (August 2022). "Emerging signals of declining forest resilience under climate change". Nature. 608 (7923): 534–539. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04959-9. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 9385496. PMID 35831499.
- News article: "Forests are becoming less resilient because of climate change". New Scientist. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- Biggs, R., et al. (2009) Turning back from the brink: Detecting an impending regime shift in time to avert it. P Natl Acad Sci Usa 106, 826–831
- Scheffer, M., et al. (2009) Early-warning signals for critical transitions. Nature 461, 53–59
- Contamin, R., and Ellison, A.M. (2009) Indicators of regime shifts in ecological systems: What do we need to know and when do we need to know it? Ecol. Appl. 19, 799–816
- Dakos, V., et al. (2010) Spatial correlation as leading indicator of catastrophic shifts. Theor Ecol 3, 163–174
- Dakos, V., et al. (2008) Slowing down as an early warning signal for abrupt climate change. P Natl Acad Sci Usa 105, 14308–14312
- van Nes, E.H., and Scheffer, M. (2007) Slow recovery from perturbations as a generic indicator of a nearby catastrophic shift. Am. Nat. 169, 738–747
- van Nes, E., and Scheffer, M. (2005) Implications of spatial heterogeneity for catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems. Ecology 86, 1797–1807
- Hastings, A., and Wysham, D.B. (2010) Regime shifts in ecological systems can occur with no warning. Ecol Lett, 1–9
- Boulton, Chris A.; Lenton, Timothy M.; Boers, Niklas (March 2022). "Pronounced loss of Amazon rainforest resilience since the early 2000s". Nature Climate Change. 12 (3): 271–278. Bibcode:2022NatCC..12..271B. doi:10.1038/s41558-022-01287-8. ISSN 1758-6798. S2CID 234889502.
- News article about the study: "Climate crisis: Amazon rainforest tipping point is looming, data shows". The Guardian. 7 March 2022. Retrieved 18 April 2022.