Blue-black grosbeak
The blue-black grosbeak (Cyanoloxia cyanoides) is a species of songbird in the family Cardinalidae.
| Blue-black grosbeak | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Male (above) and female (below) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Cardinalidae |
| Genus: | Cyanocompsa |
| Species: | C. cyanoides |
| Binomial name | |
| Cyanocompsa cyanoides (Lafresnaye, 1847) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Cyanoloxia cyanoides | |
The South American Classification Committee of the American Ornithological Society places this species in genus Cyanoloxia.[2] In addition, in 2018 the committee split the eastern lowland population into a new species, Amazonian grosbeak (Cyanoloxia rothschildii).[2]
Taxonomy and systematics
The blue-black grosbeak is found in the family Cardinalidae, within the order Passeriformes. Although it is still sometimes placed in the genus Cyanocompsa, it was found that this genus is paraphyletic and contains members of the genus Amaurospiza and Cyanoloxia.[3]
There are three subspecies in this taxa: Cyanoloxia cyanoides cyanoides, Cyanoloxia cyanoides caerulescens, and Cyanoloxia cyanoides concreta. Although these three subspecies are very similar, there are slight differences between them. Males all have dark blue plumage, however, C.c. concreta has the darkest of the three and is also the largest. Next, in terms of size and coloration, is C.c. caerulescens, followed by C.c. cyanoides, which has the smallest size and brightest plumage.[4][5]
Originally there was a fourth subspecies, C.c. rothschildii, the only subspecies found to the east of the Andes.[4] However, after examining the genetics of this subspecies, it was determined that C.c. rothschildii would be considered a separate species, Cyanoloxia rothschildii.[2]
Description
The blue-black grosbeak is sexually dimorphic. Females have dark brown plumage which can have a slight reddish hue. Males are dark blue with lighter blue eyebrows and shoulder patches on their wings. The forehead, the area just above the beak, is also a lighter shade of blue.[6][7]
Vocalization
Often blue-black grosbeaks will not be seen since they prefer to stay hidden among the vegetation, so most of the time their presence is known only when they vocalize. Their song is composed of about six whistles with decreasing pitch and ends with a "seee seee sewee suwee sweet suuu."[8] There are slight differences in the songs between the three different subspecies.[7][4]
The call is a sharp "shek" or "chit" and will often be repeated many times.[8]
Distribution and habitat
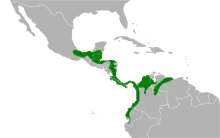
The distribution of the blue-black grosbeak is limited to the Central and South American. It is found in Belize, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, and Venezuela.[9]
Both C.c. caerulescens and C.c. concreta are found in Mexico and Central America, while C.c. cyanoides can be found from Panama to northern South America.[4]
They prefer habitats which are dense with tall trees and undergrowth because this provides sufficient cover. Although not generally seen, the blue-black grosbeak can be found at edges of broadleaf forests.[7][8]
Behaviour
Breeding
The blue-black grosbeak construct little cup nests to lay their eggs in and normally have a clutch size of 2.[10] The breeding season of the blue-black grosbeak takes place during the spring and summer months, however the peak period of the breeding season differs slightly between populations located in different areas.[6]
Gallery
 Male in Costa Rica
Male in Costa Rica_(7264648726).jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp) Blue-black grosbeak, El Tapir, Costa Rica
Blue-black grosbeak, El Tapir, Costa Rica
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Cyanoloxia cyanoides". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- "Updates & Corrections – August 2018 | Clements Checklist". www.birds.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2018-10-15.
- Klicka, John; Burns, Kevin; Spellman, Garth M. (2007). "Defining a monophyletic Cardinalini: A molecular perspective". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 45 (3): 1014–1032. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.550.1550. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2007.07.006. ISSN 1055-7903. PMID 17920298.
- García, Natalia C.; Barreira, Ana S.; Lavinia, Pablo D.; Tubaro, Pablo L. (2016-06-01). "Congruence of phenotypic and genetic variation at the subspecific level in a Neotropical passerine". Ibis. 158 (4): 844–856. doi:10.1111/ibi.12386. ISSN 0019-1019.
- Stoddard, Mary Caswell; Prum, Richard O. (2008). "Evolution of Avian Plumage Color in a Tetrahedral Color Space: A Phylogenetic Analysis of New World Buntings". The American Naturalist. 171 (6): 755–776. doi:10.1086/587526. ISSN 0003-0147. PMID 18419340. S2CID 16876611.
- "Blue-black Grosbeak - Introduction". Neotropical Birds Online. Retrieved 2018-10-15.
- Hilty, Steven L. (2003). Birds of Venezuela. Gwynne, John A., Tudor, Guy., Grajal, Alejandro., McQueen, Larry B., Webb, Sophie., Kleinbaum, Michel (2nd ed.). Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9781400834099.
- Vallely, A.C.; Dyer, D. (2018). Birds of Central America : Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691184159.
- BirdLife International (2017). "Cyanoloxia cyanoides". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T103810895A119455700. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T103810895A119455700.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- Skutch, Alexander F. (1985). "Clutch Size, Nesting Success, and Predation on Nests of Neotropical Birds, Reviewed". Ornithological Monographs (36): 575–594. doi:10.2307/40168306. JSTOR 40168306.
Further reading
- Bryson, R.W. Jr; Chaves, J.; Smith, B.T.; Miller, M.J.; Winker, K.; Pérez-Emán, J.L.; Klicka, K. (2014). "Diversification across the New World within the 'blue' cardinalids (Aves: Cardinalidae)". Journal of Biogeography. 41 (3): 587–599. doi:10.1111/jbi.12218. S2CID 56287512.
- Skutch, Alexander F. (1954). "Blue-black grosbeak" (PDF). Life Histories of Central American Birds. Pacific Coast Avifauna, Number 31. Berkeley, California: Cooper Ornithological Society. pp. 50–61.
