Cyclops (copepod)
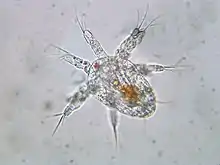
Cyclops is one of the most common genera of freshwater copepods, comprising over 400 species.[1][2] Together with other similar-sized non-copepod fresh-water crustaceans, especially cladocera, they are commonly called water fleas. The name Cyclops comes from the Cyclops of Greek mythology, as they have a single large eye; in Cyclops, the eye may be either red or black.
| Cyclops | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Copepoda |
| Order: | Cyclopoida |
| Family: | Cyclopidae |
| Genus: | Cyclops O. F. Müller, 1785 [1] |
| Synonyms | |
| |

Anatomy
Cyclops individuals may range from ½–5 mm long[3] and are clearly divided into two sections. The broadly oval front section comprises the head and the first five thoracic segments. The hind part is considerably slimmer and is made up of the sixth thoracic segment and the four legless pleonic segments. Two caudal appendages project from the rear. Although they may be difficult to observe, Cyclops has 5 pairs of legs. The long first antennae, 2 in number, are used by the males for gripping the females during mating. Afterwards, the female carries the eggs in two small sacs on her body. The larvae, or nauplii, are free-swimming and unsegmented.
Habitat
Cyclops has a cosmopolitan distribution in fresh water, but is less frequent in brackish water. It lives along the plant-covered banks of stagnant and slow-flowing bodies of water, where it feeds on small fragments of plant material, animals (such as nematodes), or carrion. It swims with characteristic jerky movements. Cyclops has the capacity to survive unsuitable conditions by forming a cloak of slime. Average lifespan is about 3 months.
Public health importance
Cyclops is intermediate host of dracunculiasis (guinea-worm disease) and fish tapeworm (Diphyllobothrium latum) infection. This disease can be passed to humans through drinking infected water. Dracunculiasis will rarely cause death but is a weakening disease.[4]
Control methods
Cyclops can be controlled using physical, chemical, biological and engineering methods.
Physical
Straining of water through piece of fine cloth is sufficient to remove Cyclops. It can also be killed by boiling water, as it is easily killed by heat at 60 °C.
Chemical
Chlorine in strength of 22 ppm destroys Cyclops in 2 hours;[5] although this concentration of chlorine gives bad odour and taste to water. Excess chlorine can be removed with Sodium thiosulfate. Calcium hydroxide at dosage of 4 gram per gallon of water can be used. Temefos kills cyclops at concentration of 1 mg/litre.
Biological
Small fish, like barbel and Gambusia, feed on Cyclops. This type of predation was used in the South Indian state of Karnataka to eradicate dracunculiasis.[6] Additionally, cyclops are widely sold in frozen packages at pet shops and fish stores as a supplemental fish food.
Species
- Cyclops abnobensis Brehm, 1958
- Cyclops abyssicola Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops abyssorum G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops acanthoides Douwe, 1914
- Cyclops adolescens Herrick, 1882
- Cyclops aequoreus Fischer, 1860
- Cyclops affinis G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops africanus Bourne, 1893
- Cyclops agilis Koch, 1838
- Cyclops agiloides G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops alajensis Ulyanin, 1874
- Cyclops albicans G. W. Smith, 1909
- Cyclops albidus Jurine, 1820
- Cyclops alius Kiefer, 1935
- Cyclops alpestris Daday, 1885
- Cyclops alticola Kiefer, 1935
- Cyclops americanus Marsh, 1893
- Cyclops amoenus Mann, 1940
- Cyclops anceps (Richard, 1897)
- Cyclops angustus S. Grassel, 1999
- Cyclops ankyrae Mann, 1940
- Cyclops anninae Menzel, 1926
- Cyclops annulatus Wierzejski, 1893
- Cyclops annulicornis Koch, 1838
- Cyclops anophthalmus Joseph, 1882
- Cyclops argulus (Fabricius, 1793)
- Cyclops armatus Tilesius, 1815
- Cyclops arnaudi G. O. Sars, 1908
- Cyclops aspericornis Daday, 1906
- Cyclops ater Herrick, 1882
- Cyclops attenuatus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops aurantius Fischer, 1860
- Cyclops australis King, 1855
- Cyclops baicalensis Vassilieva, 1950
- Cyclops bathybius Daday, 1896
- Cyclops bicolor G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops bicuspidatus Claus, 1857
- Cyclops bisetosus Rehberg, 1880
- Cyclops bissextilis Willey, 1925
- Cyclops bistriatus Koch, 1838
- Cyclops bodamicus Vosseler, 1886
- Cyclops bodanus Kiefer, 1954
- Cyclops bogoriensis Menzel, 1926
- Cyclops bohater Kozminski, 1933
- Cyclops bohemicus Srámek-Husek, 1938
- Cyclops bopsini Studer, 1878
- Cyclops brachypus (Kiefer, 1955)
- Cyclops bracteatus (O. F. Müller, 1776)
- Cyclops brasiliensis Dana, 1849
- Cyclops brehmi (Kiefer, 1927)
- Cyclops brevicaudatus Claus, 1857
- Cyclops brevicornis Baird, 1835
- Cyclops brevicornis Claus, 1857
- Cyclops brevipes Brady, 1910
- Cyclops brevisetosus Daday, 1885
- Cyclops brevispinosus Herrick, 1884
- Cyclops brucei T. Scott, 1899
- Cyclops buxtoni Gurney, 1921
- Cyclops cabanensis Russki, 1889
- Cyclops caeruleus O. F. Müller, 1776
- Cyclops canadensis Einsle, 1988
- Cyclops canthocarpoides Fischer, 1851
- Cyclops capillatus G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops capilliferus S. A. Forbes, 1893
- Cyclops carolinianus Yeatman, 1944
- Cyclops caspicus Lindberg, 1942
- Cyclops castor Desmarest, 1825
- Cyclops caudatus (G. O. Sars, 1927)
- Cyclops cavernarum Ulrich, 1902
- Cyclops ceibaensis Marsh, 1919
- Cyclops cerberus Chappuis, 1934
- Cyclops charon Kiefer, 1931
- Cyclops chelifer O. F. Müller, 1776
- Cyclops chiltoni G. M. Thomson, 1883
- Cyclops christianensis Boeck, 1872
- Cyclops ciliatus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops clandestinus Yeatman, 1964
- Cyclops claudiopolitanus Daday, 1885
- Cyclops clausii Lubbock, 1863
- Cyclops clausii Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops claviger O. F. Müller, 1785
- Cyclops coecus Pratz, 1866
- Cyclops coeruleus O. F. Müller, 1785
- Cyclops colchidanus Borutsky, 1930
- Cyclops columbianus Grassel, 1956
- Cyclops communis Lindberg, 1938
- Cyclops compactus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops coronatus Claus, 1857
- Cyclops crassicaudis G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops crassicaudoides Kiefer, 1928
- Cyclops crassicornis O. F. Müller, 1785
- Cyclops crinitus Graeter, 1910
- Cyclops croaticus Krmpotic, 1924
- Cyclops cunningtoni G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops curticaudus Dana, 1847
- Cyclops curticornis O. F. Müller, 1785
- Cyclops cyprinaceus (Shaw, 1789)
- Cyclops davidi Chappuis, 1922
- Cyclops delachauxi Kiefer, 1925
- Cyclops delphinus (O. F. Müller, 1785)
- Cyclops demetiensis Scourfield, 1932
- Cyclops dengizicus Lepeshkin, 1900
- Cyclops dentatimanus Marsh, 1913
- Cyclops dentatus Rehberg, 1880
- Cyclops dentatus Koch, 1844
- Cyclops denticulatus Nicolet, 1849
- Cyclops depressus Baird, 1837
- Cyclops diaphanus Fischer, 1853
- Cyclops diminuta Lindberg, 1937
- Cyclops dimorphus Kiefer, 1934
- Cyclops distans Kiefer, 1956
- Cyclops distinctus Richard, 1887
- Cyclops diversus (Kiefer, 1935)
- Cyclops divulsus Lindberg, 1956
- Cyclops donnaldsoni Chappuis, 1929
- Cyclops dubitabilis Kiefer, 1934
- Cyclops dubius G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops dulvertonensis G. W. Smith, 1909
- Cyclops dumasti Joly, 1883
- Cyclops dybowskii Landé, 1890
- Cyclops eboracensis Brady, 1902
- Cyclops echinatus Kiefer, 1926
- Cyclops ecornis Tilesius, 1819
- Cyclops edax S. A. Forbes, 1890
- Cyclops elegans Herrick, 1884
- Cyclops elgonensis Kiefer, 1932
- Cyclops elongatus Claus, 1863
- Cyclops emini Mrázek, 1898
- Cyclops entzii Daday, 1885
- Cyclops euacanthus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops ewarti Brady, 1888
- Cyclops exiguus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops exilis Coker, 1934
- Cyclops exsulis Gauthier, 1951
- Cyclops falsus Kiefer, 1929
- Cyclops fasciacornis Cragin, 1883
- Cyclops fedtschenkoi Ulyanin, 1875
- Cyclops feuerborni Kiefer, 1933
- Cyclops fimbriatus Fischer, 1853
- Cyclops finmarchicus O. F. Müller, 1776
- Cyclops fischeri Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops flexipes Kokubo, 1912
- Cyclops fluviatilis Herrick, 1882
- Cyclops foliaceus (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Cyclops forbesi Herrick, 1895
- Cyclops formosanus Harada, 1931
- Cyclops fragilis Kiefer, 1926
- Cyclops franciscoloi Brian, 1951
- Cyclops frivaldszkyi Daday, 1885
- Cyclops furcatus Baird, 1837
- Cyclops furcifer Claus, 1857
- Cyclops furi Kozhova & Pavlov, 1986
- Cyclops fuscus Jurine, 1820
- Cyclops gauthieri Green, 1963
- Cyclops gemellus (Gurney, 1928)
- Cyclops geoffroyi Samouelle, 1819
- Cyclops gibbus (Philippi, 1843)
- Cyclops gibsoni Brady, 1904
- Cyclops gigas Claus, 1857
- Cyclops glacialis Brady, 1910
- Cyclops gnatho (Philippi, 1843)
- Cyclops gracilicornis Landé, 1891
- Cyclops gracilis Lilljeborg, 1853
- Cyclops graeteri Chappuis, 1927
- Cyclops grandis Kiefer, 1935
- Cyclops grandispinifer Lindberg, 1940
- Cyclops gredleri Heller, 1871
- Cyclops gyrinus S. A. Forbes, 1890
- Cyclops hadjebensis Kiefer, 1926
- Cyclops halepensis Chappuis, 1922
- Cyclops hamatus Sovinsky, 1888
- Cyclops harpacticoides Shmankevich, 1875
- Cyclops haueri Kiefer, 1931
- Cyclops heberti Einsle, 1996
- Cyclops helgolandicus Rehberg, 1880
- Cyclops helleri Brady, 1878
- Cyclops horvathii Daday, 1885
- Cyclops hungaricus Daday, 1885
- Cyclops hutchinsoni Kiefer, 1936
- Cyclops hypogeus Kiefer, 1930
- Cyclops ignaeus Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops igneus Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops incertus Wolf, 1905
- Cyclops indolusitanicus Lindberg, 1938
- Cyclops inermis Tilesius, 1812
- Cyclops infernus Kiefer, 1930
- Cyclops ingens Herrick, 1882
- Cyclops inopinatus (G. O. Sars, 1927)
- Cyclops inopinus Kiefer, 1926
- Cyclops insectus S. A. Forbes, 1882
- Cyclops insignis Claus, 1857
- Cyclops intermedius Sovinsky, 1888
- Cyclops isodactylus (Philippi, 1843)
- Cyclops jashnovi Streletskaya, 1990
- Cyclops javanus Kiefer, 1930
- Cyclops jeanneli Chappuis, 1929
- Cyclops johnstoni Baird, 1834
- Cyclops josephi Moniez, 1887
- Cyclops juri Parveen, Mahoon & Saleem, 1990
- Cyclops karamani Kiefer, 1932
- Cyclops karvei Kiefer & Moorthy, 1935
- Cyclops kaufmanni Ulyanin, 1875
- Cyclops kentanensis Harada, 1931
- Cyclops kieferi Chappuis, 1925
- Cyclops kievensis Sovinsky, 1887
- Cyclops kikuchii Smirnov, 1932
- Cyclops kolensis Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops korostyschevi Sovinsky, 1888
- Cyclops kozminskii Lindberg, 1942
- Cyclops krillei Studer, 1878
- Cyclops lacinulatus O. F. Müller, 1776
- Cyclops lacunae Lowndes, 1926
- Cyclops lacustris G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops ladakanus Kiefer, 1936
- Cyclops laevimargo G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops landei Mahoon & Zia, 1985
- Cyclops languidoides Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops languidulus Willey, 1925
- Cyclops languidus (G. O. Sars, 1863)
- Cyclops lascivus Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops laticauda Templeton, 1836
- Cyclops latipes Lowndes, 1927
- Cyclops latissimus Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops laurenticus Lindberg, 1956
- Cyclops learii Ulrich, 1902
- Cyclops leewenhoekii Hoek, 1878
- Cyclops leptopus Kiefer, 1927
- Cyclops leuckarti Claus, 1857
- Cyclops lilljeborgi G. O. Sars, 1918
- Cyclops linjanticus Kiefer, 1928
- Cyclops littoralis Brady, 1872
- Cyclops lobulosus Ekman, 1905
- Cyclops longicaudatus Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops longispina Templeton, 1836
- Cyclops longistylis Brady, 1907
- Cyclops lubbocki Brady, 1869
- Cyclops lucidulus Koch, 1838
- Cyclops maarensis Vosseler, 1889
- Cyclops macleayi Dana, 1847
- Cyclops macruroides Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops macrurus G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops macuroides Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops madagascariensis Kiefer, 1926
- Cyclops magniceps Lilljeborg, 1853
- Cyclops magnoctavus Cragin, 1883
- Cyclops magnus (Marsh, 1920)
- Cyclops malayicus Kiefer, 1930
- Cyclops margaretae Lindberg, 1938
- Cyclops margoi Daday, 1885
- Cyclops marinus Prestandrea, 1833
- Cyclops matritensis Velasquez, 1941
- Cyclops mendocinus Wierzejski, 1893
- Cyclops menzeli Kiefer, 1926
- Cyclops meridianus Kiefer, 1926
- Cyclops michaelseni Mrázek, 1901
- Cyclops micropus Kiefer, 1932
- Cyclops miles Nicolet, 1849
- Cyclops miniatus Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops minimus Kiefer, 1933
- Cyclops minnilus S. A. Forbes, 1893
- Cyclops minuticornis O. F. Müller, 1785
- Cyclops minutissimus Kiefer, 1933
- Cyclops minutus Claus, 1863
- Cyclops minutus O. F. Müller, 1776
- Cyclops modestus Herrick, 1883
- Cyclops moghulensis Lindberg, 1939
- Cyclops monacanthus Kiefer, 1928
- Cyclops monardi Perret, 1925
- Cyclops mongoliensis Einsle, 1992
- Cyclops mulleri Ferussac, 1806
- Cyclops muscicola Menzel, 1926
- Cyclops muscicolus Lastochkin, 1927
- Cyclops nanus G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops naviculus Say, 1818
- Cyclops navus Herrick, 1882
- Cyclops nearcticus Kiefer, 1934
- Cyclops necessarius Kiefer, 1926
- Cyclops neglectus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops neumani Pesta, 1927
- Cyclops neymanae Streletskaya, 1990
- Cyclops niceae Mann, 1940
- Cyclops nigeriae Brady, 1910
- Cyclops nigricauda Norman, 1869
- Cyclops nivalis Daday, 1885
- Cyclops novaezealandiae G. M. Thomson, 1879
- Cyclops nubicus Chappuis, 1922
- Cyclops obesicornis Templeton, 1836
- Cyclops obsoletus Koch, 1838
- Cyclops ochridanus Kiefer, 1932
- Cyclops odessanus Shmankevich, 1875
- Cyclops oithonoides G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops oligarthrus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops operculatus Chappuis, 1917
- Cyclops orientalis Ulyanin, 1875
- Cyclops ornatus Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops ovalis Brady, 1872
- Cyclops pachycomus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops pallidus Norman, 1869
- Cyclops paludicola Herbst, 1959
- Cyclops palustris Sovinsky, 1888
- Cyclops panamensis Marsh, 1913
- Cyclops papuanus Daday, 1901
- Cyclops paradyi Daday, 1885
- Cyclops paraplesius Kiefer, 1929
- Cyclops parcus Herrick, 1882
- Cyclops pauper Fric, 1871
- Cyclops pectinatus Herrick, 1883
- Cyclops pectinifer Cragin, 1883
- Cyclops pelagicus (Rose, 1929)
- Cyclops pennatus Claus, 1857
- Cyclops pentagonus Vosseler, 1886
- Cyclops perarmatus Cragin, 1883
- Cyclops phaleratus Koch, 1838
- Cyclops phaleroides Labbé, 1927
- Cyclops philippinensis Marsh, 1932
- Cyclops phreaticus Chappuis, 1928
- Cyclops pictus Koch, 1838
- Cyclops pilosus Kiefer, 1934
- Cyclops piscinus (Linnaeus, 1761)
- Cyclops planus Gurney, 1909
- Cyclops plumosus (Philippi, 1843)
- Cyclops poggenpolii Sovinsky, 1888
- Cyclops poppei Rehberg, 1880
- Cyclops potamius Burckhardt, 1913
- Cyclops prasinus Fischer, 1860
- Cyclops prealpinus Kiefer, 1939
- Cyclops procerus Herbst, 1955
- Cyclops productus (O. F. Müller, 1785)
- Cyclops prolatus Kiefer, 1935
- Cyclops pubescens Dana, 1847
- Cyclops purpureus (Philippi, 1843)
- Cyclops pusillus Brady, 1904
- Cyclops puteanus Frey, 1869
- Cyclops pygmaeus Rehberg, 1880
- Cyclops quadricornis (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Cyclops quinquepartitus Marsh, 1913
- Cyclops racovitzai Chappuis, 1923
- Cyclops rarispinus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops reductus Chappuis, 1925
- Cyclops restrictus Lindberg, 1948
- Cyclops ricae Monchenko, 1977
- Cyclops richardi Lindberg, 1942
- Cyclops robustus G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops roseus Daday, 1885
- Cyclops rostratus (Philippi, 1843)
- Cyclops roumaniae Cosmovici, 1900
- Cyclops royi Lindberg, 1940
- Cyclops rubellus Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops rubens O. F. Müller, 1785
- Cyclops salinus Brady, 1903
- Cyclops salmoneus (J. C. Fabricius, 1792)
- Cyclops saltatonius (O. F. Müller, 1776)
- Cyclops sanfilippoi Brian, 1951
- Cyclops sanguineus (Philippi, 1843)
- Cyclops schmeili Poppe & Mrázek, 1895
- Cyclops scourfieldi Brady, 1891
- Cyclops scutifer G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops semiserratus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops sensitivus Graeter & Chappuis, 1914
- Cyclops serratus Pratz, 1866
- Cyclops serrulatoides Labbé, 1927
- Cyclops serrulatus Fischer, 1851
- Cyclops setiger Frey, 1869
- Cyclops setosus Haldeman, 1842
- Cyclops sevani Meshkova, 1947
- Cyclops shatalovi Streletskaya, 1990
- Cyclops signatus Koch, 1838
- Cyclops silesicus Schäfer, 1934
- Cyclops silvestrii Brian, 1927
- Cyclops similis Templeton, 1836
- Cyclops simillimus Brady, 1907
- Cyclops simplex Poggenpol, 1874
- Cyclops skopljensis Kiefer, 1932
- Cyclops smirnovi Rylov, 1948
- Cyclops soli Kokubo, 1912
- Cyclops spartinus Ruber, 1966
- Cyclops speratus Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops spinifer Daday, 1902
- Cyclops spinulosus Claus, 1893
- Cyclops stagnalis Einsle, 1996
- Cyclops staheli Chappuis, 1917
- Cyclops staphylinus Desmarest, 1825
- Cyclops strenuus Fischer, 1851
- Cyclops stroemii Baird, 1834
- Cyclops stuhlmanni Mrázek, 1895
- Cyclops stygius Chappuis, 1924
- Cyclops subaequalis Kiefer, 1928
- Cyclops subterraneus Pratz, 1866
- Cyclops subtropicus Lindberg, 1937
- Cyclops sumatranus Kiefer, 1933
- Cyclops sydneyensis Schmeil, 1898
- Cyclops sylvestrii Brian, 1927
- Cyclops taipehensis Harada, 1930
- Cyclops tanganicae (Gurney, 1928)
- Cyclops tatricus Kozminski, 1927
- Cyclops tenellus G. O. Sars, 1909
- Cyclops tenuicaudis Daday, 1885
- Cyclops tenuicornis Claus, 1857
- Cyclops tenuipes (Philippi, 1843)
- Cyclops tenuis Marsh, 1910
- Cyclops tenuisaccus G. O. Sars, 1927
- Cyclops tenuissimus Herrick, 1883
- Cyclops teras Graeter, 1907
- Cyclops thomasi S. A. Forbes, 1882
- Cyclops thorace (Ström, 1770)
- Cyclops transilvanicus Daday, 1885
- Cyclops tricolor Lindberg, 1937
- Cyclops trisetosus Herbst, 1957
- Cyclops triumvirorum Kiefer, 1935
- Cyclops troglodytes Chappuis, 1923
- Cyclops troglophilus Kiefer, 1932
- Cyclops tropicus Kiefer, 1932
- Cyclops trouchanowi Sovinsky, 1888
- Cyclops uljanini Sovinsky, 1887
- Cyclops uniangulatus Cragin, 1883
- Cyclops unisetiger Graeter, 1899
- Cyclops uruguayensis Kiefer, 1935
- Cyclops varicans G. O. Sars, 1863
- Cyclops varicoides Brady, 1908
- Cyclops varius Lilljeborg, 1901
- Cyclops venustoides Coker, 1934
- Cyclops venustus Norman & T. Scott, 1906
- Cyclops vernalis Fischer, 1853
- Cyclops vicinus Ulyanin, 1875
- Cyclops viduus Kiefer, 1933
- Cyclops vincentianus Brian, 1927
- Cyclops vinceus Shmankevich, 1875
- Cyclops virescens Brady, 1910
- Cyclops viridis (Jurine, 1820)
- Cyclops viridosignatus E. F. Byrnes, 1909
- Cyclops vitiensis Dana, 1847
- Cyclops vulgaris Koch, 1838
- Cyclops wigrensis Streletskaya, 1988
- Cyclops zschokkei Graeter, 1910
References
- Daphne Cuvelier & T. Chad Walter. "Cyclops Müller, 1785". World Copepoda database.
- G. G. Marten (1986). "Issues in the development of Cyclops for mosquito control". In M. F. Uren; J. Blok; L.H. Manderson (eds.). Arbovirus Research in Australia: Proceedings of the Fifth Symposium (August 28 – September 1, 1989, Brisbane, Australia) (PDF). pp. 159–164.
- Reed & McIntyre (1995). Cyclops strenuus (Fischer, 1851) sensu lato in Alaska and Canada, with new records of occurrence
- "Cyclops" (PDF). WHO.
- MAJOR C. H H. HAROLD. "FURTHER INVESTIGATION INTO THE STERILIZATION OF WATER BY CHLORINE AND SOME OF ITS COMPOUNDS" (PDF). Militaryhealth.bmj.com. Retrieved 18 March 2022.
- USA National Research Council; World Health Organization (1985). Workshop on opportunities for control of dracunculiasis, 16–19 June 1982, Washington, D.C. Contributed papers (PDF). Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press. pp. 153–177.
- Jan A. Rozendaal; World Health Organization (1997). Vector control: methods for use by individuals and communities. World Health Organisation. ISBN 9789241544948.