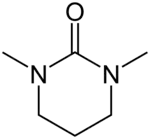
DMPU
N,N′-Dimethylpropyleneurea (DMPU) is a cyclic urea sometimes used as a polar, aprotic organic solvent. In 1985, Dieter Seebach showed that it is possible to replace the suspected carcinogen hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA) with DMPU.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Dimethyl-1,3-diazinan-2-one[1] | |
| Other names
N,N′-Dimethyl-N,N′-trimethyleneurea N,N′-Dimethylpropyleneurea 1,3-Dimethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | DMPU |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.027.841 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12N2O | |
| Molar mass | 128.175 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.064 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −20 °C; −4 °F; 253 K |
| Boiling point | 246.5 °C (475.7 °F; 519.6 K) (Source) |
| miscible | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.4875-1.4895 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H302, H318, H361f | |
| P201, P202, P264, P270, P280, P281, P301+P312, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P330, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 121 °C (250 °F; 394 K) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- Mukhopadhyay, T.; Seebach, D. (1982). "Substitution of HMPT by the cyclic urea DMPU as a cosolvent for highly reactive nucleophiles and bases". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 65 (1): 385–391. doi:10.1002/hlca.19820650141.
Further reading
- Dehmlow, E. V.; Rao, Y. R. (1988). "Phase transfer catalytic preparation of the dipolar aprotic solvents DMI and DMPU". Synthetic Communications. 18 (5): 487–494. doi:10.1080/00397918808060741.
- Anderson, J. C.; Smith, S. C. (1990). "Oxodiperoxymolybdenum(pyridine)-1,3-dimethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrahydro-2(1H)-pyrimidinone (MoO5 · Py · DMPU): A safer alternative to MoOPH for the α-hydroxylation of carbonyl compounds". Synlett. 1990 (2): 107–108. doi:10.1055/s-1990-21003.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.