DSP/BIOS Link
DSP/BIOS Link or DSPLINK is an interprocessor or inter-process communication (IPC) scheme to pass messages and data in multiprocessing systems.[1] In the case of the DaVinci digital signal processor (DSP) family from Texas Instruments, this scheme allows passing messages and data between an ARM client and a DSP server. DSPLINK can be used to implement a layer of software abstraction called a remote procedure call (RPC) that allows a remote function on the DSP to appear as local function calls in the ARM application code. The Codec Engine IPC communication layer is implemented using a RPC call scheme built on DSP/BIOS LINK.
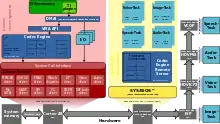
Overview
DSP/BIOS LINK is implemented using shared memory and internal interrupts from the ARM to the DSP and vice versa.
The shared memory protocol for IPC is implemented as follows:
- The ARM and DSP are programmed to a predetermined memory address where a message will be sent from the ARM to the DSP; and another for messages sent from the DSP to the ARM.
- One processor sends messages to the other by writing the message into the pre-determined address and then sending an interrupt to signal the other processor that a new message is available. When transferring data buffers, only a pointer to a given buffer needs to be passed since the buffer resides in shared memory that is accessible to both the processors. ARM buffer addresses must be translated into physical addresses when being presented to the DSP, as the DSP does not have an MMU or a concept of virtual addressing.
- Once the processor receiving the message has read it, it marks a flag in shared memory to indicate that the message memory is now available to be rewritten with another message.
The DSP included in many DaVinci-based devices generally runs TI's DSP/BIOS RTOS. When multiple, heterogeneous cores are included in the device (e.g. DM644x), DSP/BIOS Link drivers run on both the ARM processor and the DSP to provide communication between the two.
Operating systems
A number of ARM9 operating systems support DSP/BIOS Link drivers:
- Montavista Linux
- TimeSys Linux
- Mentor Graphics Nucleus OS
- Green Hills Software Integrity RTOS
- QNX Neutrino
- Windows CE
- LEOs (RTOS)
See also
External links
References
- Hartenstein, Reiner W.; Grünbacher, Herbert (2003-06-29). Field-Programmable Logic and Applications: The Roadmap to Reconfigurable Computing: 10th International Conference, FPL 2000 Villach, Austria, August 27-30, 2000 Proceedings. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-44614-9.