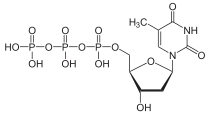
Thymidine triphosphate
Deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) is one of the four nucleoside triphosphates that are used in the in vivo synthesis of DNA. Unlike the other deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, thymidine triphosphate does not always contain the "deoxy" prefix in its name.[1] The corresponding ribonucleoside triphosphate is called uridine triphosphate.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Thymidine 5′-(tetrahydrogen triphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,5R)-5-(2,4-Dioxo-5-methyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3-hydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl} tetrahydrogen triphosphate | |
| Other names
dTTP, 2′-Deoxythymidine triphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.064 |
| MeSH | thymidine+5'-triphosphate |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H17N2O14P3 | |
| Molar mass | 482.168 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It can be used by DNA ligase to create overlapping "sticky ends" so that protruding ends of opened microbial plasmids may be closed up.
References
- Coghill, Anne M.; Garson, Lorrin R., eds. (2006). The ACS style guide: effective communication of scientific information (3rd ed.). Washington, D.C.: American Chemical Society. p. 244. ISBN 978-0-8412-3999-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.