Davallialactone
Davallialactone is a bio-active hispidin analog isolated from fungi in the genus Inonotus.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
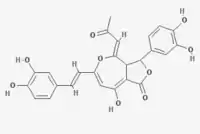
(4Z)-3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-6-[(E)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethenyl]-8-hydroxy-4-(2-oxopropylidene)-3,3a-dihydrofuro[3,4-c]oxepin-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H20O9 | |
| Molar mass | 464.426 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Risal, P; Hwang, PH; Yun, BS; Yi, HK; Cho, BH; Jang, KY; Jeong, YJ (2012). "Hispidin analogue davallialactone attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice". Journal of Natural Products. 75 (10): 1683–9. doi:10.1021/np300099a. PMID 23025331.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.