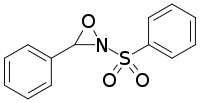
Davis reagent
Davis reagent (3-phenyl-2-(phenylsulfonyl)-1,2-oxaziridine or 2-(benzenesulfonyl)-3-phenyloxaziridine) is a reagent used for oxidation in the Davis oxidation reaction,[1] as well as oxidation of thiols to sulfones.[2] It is named for Franklin A. Davis.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(Benzenesulfonyl)-3-phenyloxaziridine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H11NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 261.30 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Davis, Franklin A.; Vishwakarma, Lal C.; Billmers, Joanne G.; Finn, John (1 August 1984). "Synthesis of α-hydroxycarbonyl compounds (acyloins): direct oxidation of enolates using 2-sulfonyloxaziridines". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 49 (17): 3241–3243. doi:10.1021/jo00191a048.
- Sandrinelli, Franck; Perrio, Stéphane; Beslin, Pierre (13 September 1999). "A New Reaction of 2-(Phenylsulfonyl)-3-phenyloxaziridine (Davis Reagent): Oxidation of Thiolates to Sulfinates. Application to the Synthesis of Sulfones". Organic Letters. 1 (8): 1177–1180. doi:10.1021/ol990170k.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.