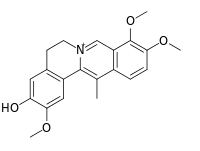
Dehydrocorybulbine
Dehydrocorybulbine (DHCB) is an alkaloid isolated from Corydalis yanhusuo.[1] Dehydrocorybulbine binds to the dopamine D1 receptor.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-2,9,10-trimethoxy-13-methyl-7,8,13,13a-tetradehydroberbin-7-ium | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-2,9,10-trimethoxy-13-methyl-5,6-dihydro-7λ5-isoquinolino[3,2-a]isoquinolin-7-ylium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H22NO4+ | |
| Molar mass | 352.40 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Research has indicated that DHCB can be helpful in reducing neuropathic pain.[2][3]
References
- Ma, ZZ; Xu, W; Jensen, NH; Roth, BL; Liu-Chen, LY; Lee, DY (2008). "Isoquinoline alkaloids isolated from Corydalis yanhusuo and their binding affinities at the dopamine D1 receptor". Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 13 (9): 2303–12. doi:10.3390/molecules13092303. PMC 6245449. PMID 18830156.
- Chinese herbal compound relieves inflammatory and neuropathic pain
- A Novel Analgesic Isolated from a Traditional Chinese Medicine. Current Biology. Volume 24, Issue 2, p117–123, 20 January 2014
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.