Determiner spreading
In linguistics, determiner spreading (DS), also known as Multiple or Double Determiners [1] is the appearance of more than one determiner associated with a noun phrase, usually marking an adjective as well as the noun itself.[2] The extra determiner has been called an adjectival determiner [3] because determiner spreading is most commonly found in adjectival phrases. Typical examples involve multiple occurrences of the definite article or definiteness marking, such is found in (but not limited to) the languages listed below. The structure of such phrases is widely discussed and there is not one conclusive analysis. Because of this, the example languages below each show unique structure where different proposed analyses have been used.
Researchers have found when a language shows ellipsis within a Determiner phrase, and in particular those with adjective phrases, determiner spreading does not occur. Due to this, we do not find determiner spreading in languages such as Romance Languages as well as English.[4]
Languages with determiner spreading
Determiner spreading in Albanian
Determiner spreading is found in Albanian where two definite articles are used for just one referent boy.[5] As shown in (1) and (2), the ordering of the noun and the adjective does not matter, as long as the determiner falls before the adjective.
| (1) | djal-i | i | mire |
| boy-the | the | good | |
| N-D | D | Adj | |
| 'the good boy'
(from Alexiadou et al. 2007:73) | |||
| (2) | i | mir-i | djalë |
| the | good-the | boy [6] | |
| D | Adj-D | N | |
| 'the good boy' | |||
In Albanian, either of these sentence constructions in (1) and (2) are grammatical to mean the good boy. In both of the sentences the determiner i marks the referent boy. It is noted that the determiner i is a morphological entity to mark the adjectival class rather than definiteness of the noun, as is found in Greek below.[7]
Modern Greek
In Modern Greek, determiner spreading is not obligatory, and it contrasts with a non-spreading example in (3):[8]
(3)
| i | orea | xoreftria |
| the | beautiful | dancer |
| i. 'the dancer who is beautiful' |
| ii. 'the dancer who dances beautifully' [9] |
The sentence above has an ambiguous meaning explained by the last two lines in the sentence above in (3). Both the meanings (i) and (ii) are grammatical with non-determiner spreading. However when DS is introduced, the sentence no longer takes on an ambiguous meaning. Determiner spreading in the example in (4) has eliminated the ambiguity, rendering the second meaning in (ii) to be ungrammatical.
(4)
| i | orea | i | xoreftria |
| the | beautiful | the | dancer |
| i. the dancer who is beautiful |
| ii. *the dancer who dances beautifully [10] |
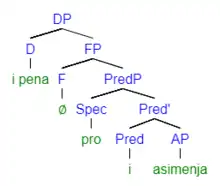
The question that is being posed in (5) requires an answer to differentiate which kind of pen, silver or gold. The response in (6) shows determiner spreading occurring because the adjective is a "restrictive modifier".[11]
(5)
| Ala | pja | pena-ti | xrisi | i | tin | asimenja? |
| but | which | pen-the | golden | or | the | silver [12] |
| 'But which pen; the gold or the silver?' |
(6)
| Nomizo | tin | asimenja | tin | pena | / | * Nomizo | tin | asimenja | pena |
| I think | the | silver | the | pen | / | * I think | the | silver | pen [13] |
Researchers believe that determiner spreading only occurs when the phrase has an "intersective reading".[14] Meaning that the focus of the sentence is the kind of pen rather than the pen itself. The determiner spreading is syntactically how a speaker can give stress to a phrase in Modern Greek. It has been suggested that the same result of focus on the type of pen can be acquired semantically by giving focus to the adjective, as marked by capital letters in (7).
(7)
| Nomizo | tin | ASIMENJA | pena |
| I think | the | SILVER | pen [15] |
A commonality between the Greek examples we have seen thus far is that determiner spreading is obligatorily definite Article (grammar) in Greek. Another language specific observation is that the determiner precedes the adjective. Researchers suggest that in order for an adjective to appear post-nominally, the determiner must precede the adjective to be grammatical in Greek. The examples below in (8) and (9) reinforce this observation showing (8) to be ungrammatical where meghalo follows spiti with no determiner intervening.
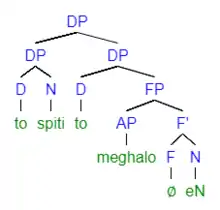
(8)
| *To | spiti | megahalo | to | petrino |
| The | house | big | the | of.stone [16] |
| 'The big stone house' |
(9)
| To | spiti | to | megahalo | to | petrino |
| The | house | the | big | the | of.stone [17] |
| 'The big stone house' |
An alternative structure to the tree above (see "the silver pen" tree), is shown to the right in "the big house". Researchers have described this structure as a predicative configuration in which the DP in SpecDP to spiti is acting as the subject of the higher DP.[18]
Swedish
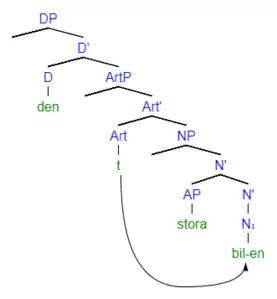
In contrast with the optional DS in Greek, Swedish phrases that have an adjective show obligatory determiner spreading.[19] Example (10) is marked as ungrammatical because it is monadic with respect to DS - there is only one determiner. By suffixing the noun with the determiner -en in example (11), the phrase becomes grammatical.
(10)
| *den | stora | bil |
| the | big | car [20] |
| 'The big car' |
(11)
| den | stora | bil-en |
| the | big | car-the [21] |
| 'The big car' |
One proposed analysis of the structure of DS in Swedish suggests that den-support, is used to support definite DPs when D cannot be satisfied in any other way. It is used as a type of feature support for definiteness; when the definite noun carries stress, den is inserted for support to the DP. The determiner den and the determiner suffix -en are in complementary distribution. This proposed structure is shown in the syntactic tree to the right; where the den has already been inserted and the -en is experiencing downward movement to suffix the noun bil.[22]
See also
Notes
- Santelmann, L. 1993:1
- Martinis, T. 2003:165-190
- Rivero, M. L., Rallē, A., & MyiLibrary. 2001:165-166, 191-192
- Phoevos Panagiotidis, E. & Marinis, T. 2011:285
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:73
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:73
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:73
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:368
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:368
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:368
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:366
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:367
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:367
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:368
- Alexiadou, A., et al. 2007:367
- Phoevos Panagiotidis, E., & Marinis, T. 2011:270
- Phoevos Panagiotidis, E., & Marinis, T. 2011:270
- Phoevos Panagiotidis, E., & Marinis, T. 2011:283
- Santelmann, L. 1993:174
- Santelmann, L. 1993:174
- Santelmann, L. 1993:174
- Santelmann, L. 1993:174
Bibliography
- Alexiadou, A., Haegeman, L., & Stavrou, M. 2007. Noun Phrase in the generative perspective. Mouton de Gruyter: Berlin.
- Phoevos Panagiotidis, E., & Marinis, T. 2011. Determiner spreading as DP‐predication. Studia Linguistica, 65(3), 268-298. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9582.2011.01186.x
- Rivero, M. L., Rallē, A., & MyiLibrary. 2001. Comparative syntax of Balkan languages. Oxford;New York;: Oxford University Press.
- Santelmann, L. 1993. The distribution of double determiners in Swedish: den support in D*. Studia Linguistica, 47: 154–176. doi:10.1111/j.1467-
9582.1993.tb00844.x
- Martinis, T. 2003. The acquisition of the DP in modern Greek. John Benjamins Publishing Company.