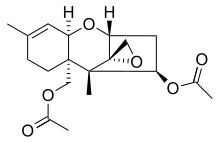
Diacetylverrucarol
Diacetylverrucarol is a natural trichothecene produced by the fungus Myrothecium verrucaria. Chemically, it is an acetate derivative of verrucarol.
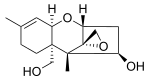 Verrucarol
Verrucarol
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
12α,13-Epoxytrichothec-9-ene-4β,15-diyl diacetate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,2′S,4R,5S,5aR,9aR)-5a-[(Acetyloxy)methyl]-5,8-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,5a,6,7,9a-octahydrospiro[[2,5]methano[1]benzoxepine-10,2′-oxiran]-4-yl acetate | |
| Other names
12,13-Epoxy-trichothec-9-ene-4,15-diol diacetate; 4,15-Diacetylverrucarol; Antibiotic A 2; Di-O-acetylverrucarol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.354 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H26O6 | |
| Molar mass | 350.411 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H300, H310, H315, H319, H330, H335 | |
| P260, P261, P262, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P350, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P320, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P361, P362, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Herbicide use
Trichothecenes have been found to cause growth retardation, wilting, chlorosis, and necrosis in some plants.[1] It can work in poor conditions, even where there is very little or no moisture. Diacetylverrucarol is undergoing study for its successful effects at reducing or killing the kudzu weed. It is prepared through liquid fermentation of Myrothecium verrucaria mycelium after which it can be used as a pesticide. This causes very little harm to the plants that the kudzu plant displaces. Results appeared within 24 hours and the kudzu plant's roots were diseased after 14 days. In greenhouse experiments the fungus killed 100 percent of the kudzu seeds, and, in outdoor trials, 90-100 percent of older plants. The fungus is undergoing study to reduce the diacetylverrucarol presence to reduce side effects.[2]
Because it is a trichothecene, it has significant toxicity. If swallowed by humans, the initial symptoms are general discomfort, dry eyes, and drowsiness. If a larger dose is consumed, symptoms of a hemorrhagic fever will occur, as well as mental impairment. Other animals are susceptible as well, and can experience growth retardation, reproductive disorders, and vomiting if the substance is consumed.[1][3]
References
- Rocha, O.; K. Ansari; F. M. Doohan (April 2005). "Effects of trichothecene mycotoxins on eukaryotic cells: A review". Food Additives and Contaminants. University College Dublin: Taylor & Francis. 22 (4): 369–378. doi:10.1080/02652030500058403. PMID 16019807. S2CID 1534222.
- Jan Suszkiw (July 2009). "Kudzu". Agricultural Research. 57: 4–5.
- Boyette, C. Douglas; H. Lynn Walker; Hamed K. Abbas (April 2005). "Biological Control of Kudzu (Pueraria lobata) with an Isolate of Myrothecium verrucaria". Biocontrol Science & Technology. Taylor & Francis. 12: 75–82. doi:10.1080/09583150120093031. S2CID 54188453.