Difluoroacetic acid
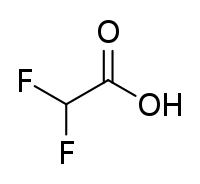
Difluoroacetic acid is a chemical compound with formula CHF2COOH. It is a dihalogenocarboxylic acid, specifically a structural analog of acetic acid with two of three hydrogen atoms on the alpha carbon replaced with fluorine atoms. In solution, it dissociates to form difluoroacetate ions. Difluoroacetic acid can also be used as direct C-H difluoromethylating reagent.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Difluoroacetic acid | |
| Other names
2,2-Difluoroacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.218 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2F2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 96.033 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.526 g/mL[1] |
| Melting point | −1 °C (30 °F; 272 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 132–134 °C (270–273 °F; 405–407 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- "Difluoroacetic acid". Sigma-Aldrich.
- Tung, Truong Thanh; Christensen, Søren Brøgger; Nielsen, John (2017). "Difluoroacetic Acid as a New Reagent for Direct C-H Difluoromethylation of Heteroaromatic Compounds". Chemistry - A European Journal. 23 (72): 18125–18128. doi:10.1002/chem.201704261. PMID 28945302.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.