Diisopropylbenzenes
In organic chemistry, the diisopropylbenzenes constitute a group of aromatic hydrocarbons, whose chemical structure consists of a benzene ring (C6H6) with two isopropyl groups (−CH(CH3)2) as substituents. Through their different arrangement, they form three structural isomers with the molecular formula C12H18.
| Diisopropylbenzenes | |||
| Systematic name | 1,2-Diisopropylbenzene | 1,3-Diisopropylbenzene | 1,4-Diisopropylbenzene |
| Common name | o-Diisopropylbenzene | m-Diisopropylbenzene | p-Diisopropylbenzene |
| Chemical structure | 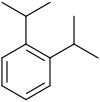 |
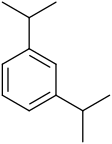 |
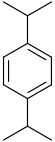 |
| CAS Number | 577-55-9 | 99-62-7 | 100-18-5 |
| PubChem | CID 11345 from PubChem | CID 7450 from PubChem | CID 7486 from PubChem |
| Chemical formula | C12H18 | ||
| Molar mass | 162.28 g/mol | ||
| State of matter | Liquid | ||
| Melting point | −57 °C[1] | −63 °C[2] | −17 °C[3] |
| Boiling point | 205 °C[1] | 203 °C[2] | 210 °C[3] |
| Solubility | Very slightly soluble in water[1] | 0.072 mg·l−1 in water (25 °C)[2] | Practically insoluble in water[3] |
References
External links
 Media related to Diisopropylbenzenes at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Diisopropylbenzenes at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.