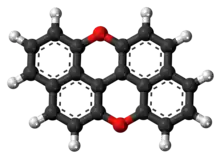
Dinaphthylene dioxide
Dinaphthylene dioxide, also known as peri-xanthenoxanthene (PXX), is an organic compound used to synthesize 3,9-diphenyl-peri-xanthenoxanthene (Ph-PXX). Ph-PXX, in its soluble form, is used as organic semiconductor for thin-film transistors (TFT).[2]
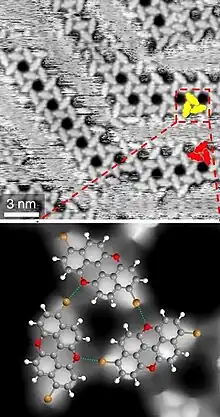
STM images of brominated PXX molecules
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
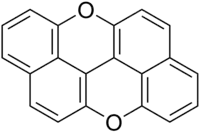
| Preferred IUPAC name
Xantheno[2,1,9,8-klmna]xanthene | |
| Other names
Dinaphthalene dioxide peri-Xanthenoxanthene (2,8');(8,2')-dioxo-1,1'-binaphthyl NSC47493 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 282.298 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Dinaphthylene dioxide, PubChem
- Kobayashi, N.; Sasaki, M.; Nomoto, K. (2009). "Stableperi-Xanthenoxanthene Thin-Film Transistors with Efficient Carrier Injection". Chemistry of Materials. 21 (3): 552–556. doi:10.1021/cm802826m.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.