Dinitroaniline
Dinitroanilines are a class of chemical compounds with the chemical formula C6H5N3O4. They are derived from both aniline and dinitrobenzenes. There are six isomers: 2,3-dinitroaniline, 2,4-dinitroaniline, 2,5-dinitroaniline, 2,6-dinitroaniline, 3,4-dinitroaniline, and 3,5-dinitroaniline.
Dinitroanilines are intermediates in the preparation of various industrially important chemicals including dyes and pesticides. Herbicides which are derivatives of dinitroanilines include benfluralin, butralin, chlornidine, dinitramine, dipropalin, ethalfluralin, fluchloralin, isopropalin, methalpropalin, nitralin, oryzalin, pendimethalin, prodiamine, profluralin, and trifluralin.
2,4-Dinitroaniline can be prepared by reaction of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene with ammonia or by acid hydrolysis of 2,4-dinitroacetanilide.[1]
Dinitroanilines are explosive and flammable with heat or friction.
Dinitroanilines were developed prior to 2015 by, among others, the Dow Chemical Company, who then sold their business to privately-held Gowan Company.[2]
| Dinitroanilines | ||||||
| Chemical name | 2,3-Dinitroaniline | 2,4-Dinitroaniline | 2,5-Dinitroaniline | 2,6-Dinitroaniline | 3,4-Dinitroaniline | 3,5-Dinitroaniline |
| Alternate name | 2,3-Dinitro-1-aminobenzene 2,3-Dinitrophenylamine 2,3-Dinitraniline |
2,4-Dinitro-1-aminobenzene 2,4-Dinitrophenylamine 2,4-Dinitraniline |
2,5-Dinitro-1-aminobenzene 2,5-Dinitrophenylamine 2,5-Dinitraniline |
2,6-Dinitro-1-aminobenzene 2,6-Dinitrophenylamine 2,6-Dinitraniline |
3,4-Dinitro-1-aminobenzene 3,4-Dinitrophenylamine 3,4-Dinitraniline |
3,5-Dinitro-1-aminobenzene 3,5-Dinitrophenylamine 3,5-Dinitraniline |
| Chemical structure | 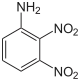 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| CAS Number | 602-03-9 | 97-02-9 | 619-18-1 | 606-22-4 | 610-41-3 | 618-87-1 |
| 26471-56-7 (isomeric mixture) | ||||||
| PubChem | CID 136400 from PubChem | CID 7321 from PubChem | CID 123081 from PubChem | CID 69070 from PubChem | CID 136407 from PubChem | CID 12068 from PubChem |
| Chemical formula | C6H5N3O4 | |||||
| Molar mass | 183.12 g/mol | |||||
| Appearance | colorless to yellowish combustible powder | |||||
| Melting point | 187.8 °C[3] | 136 °C (decomp.)[4] | 154–158 °C | 160–162 °C[5] | ||
| Density | 1.646 g/cm (50 °C)[6] | 1.61 g/cm[3] | 1.736 g/cm | 1.601 g/cm (50 °C)[6] | ||
| Solubility | soluble in water (1–2 g/L at 20 °C) | |||||
| GHS hazard pictograms |
    [3] [3] |
   [4] [4] |
   |
   [5] [5] | ||
| H- and P-phrases | H300, H310, H330, H373, H411 | H302, H311, H332, H373 | H301, H311, H331, H373 | H301, H311, H331, H373 | ||
| P260, P264, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310 | P260, P301+P310, P320, P361, P405, P501 | P261, P280, P301+P310, P311 | P261, P280, P301+P310, P311 | |||
References
- WO 1991001292 Method for the Preparation of Nitroanilines
- dowagro.com: "Gowan Company, L.L.C. Agrees to Acquire Global DNA Business from Dow AgroSciences LLC", 30 Nov 2015
- Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- "3,5-Dinitroaniline". Sigma-Aldrich.
- C. L. Yaws (2008). Thermophysical properties of chemicals and hydrocarbons (1st ed.). New York: William Andrew Inc. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-815-51596-8.