Diterpene alkaloids
Diterpene alkaloids are natural products of the terpene alkaloid type.[1]

Occurrence
Veatchine is found in the bark of Garrya veatchii, a member of the Cup Catkins family.[2] Aconitine is the main alkaloid in aconite.[3]
Structure
Diterpene alkaloids can be divided into two groups: The diterpene alkaloids, characterized by a C20 parent body, and the norditerpene alkaloids, which are based on a hexacyclic C19 parent body.[1]
Representatives
Diterpene group
Among the C20 alkaloids is the atisine-type (atisine, hetidine, hetisine) and the veatchine-type (Veatchin, Napellin).[1]
 Atisine
Atisine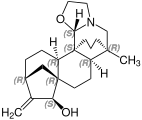 Veatchin
Veatchin
Northern iterpene group
The C19 alkaloids include, among others, the aconitine type (aconitine, delphinine) and the lycoctonine type (Lycoctonin, Browniin).[1]
-Lycoctonine_Structural_Formula_V2.svg.png.webp) (+)-Lycoctonine
(+)-Lycoctonine
Properties
Aconitine has cardiac arrhythmic and antipyretic properties and is one of the most toxic plant compounds.[2]
References
- Entry on Diterpen-Alkaloide. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved {{{Datum}}}.
- Eberhard Breitmaier (1997), Alkaloide, Wiesbaden: Springer Fachmedien, pp. 83f., ISBN 9783519035428
- Rudolf Hänsel, Otto Sticher (2007), Pharmakognosie Phytopharmazie (8 ed.), Heidelberg: Springer Medizin Verlag, p. 1466, ISBN 9783540265085
.jpg.webp)