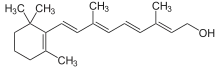
Diterpene
Diterpenes are a class of terpenes composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary intermediate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol. They are known to be antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory.[1][2]

Structures
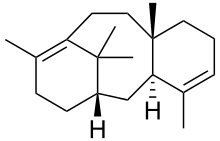
As with most terpenes a huge number of potential structures exists, which may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present.
| Number of rings | Examples |
|---|---|
| 0 | Phytane |
| 1 | Cembrene A |
| 2 | Sclarene, Labdane |
| 3 | Abietane, Taxadiene |
| 4 | Stemarene, Stemodene |
Biosynthesis
Diterpenes are derived from the addition of one IPP unit to FPP to form geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). From GGPP, structural diversity is achieved mainly by two classes of enzymes; the diterpene synthases and cytochromes P450. Several diterpenes are produced by plants and cyanobacteria. GGPP is also the precursor for the synthesis of the phytane by the action of the enzyme geranylgeranyl reductase. This compound is used for the biosynthesis of tocopherols and the phytyl functional group is used in the formation of chlorophyll a, ubiquinones, plastoquinone and phylloquinone.[3]
Diterpenoids
Diterpenes are formally defined as being hydrocarbons and thus contain no heteroatoms. Functionalized structures should instead be called diterpenoids, although in scientific literature the two terms are often used interchangeably. Although a wide range of terpene structures exist, few of them are biologically significant; by contrast, diterpenoids possess a rich pharmacology and include important compounds such as retinol, phytol or taxadiene.
Taxanes
Taxanes are class of diterpenoids featuring a taxadiene core. They are produced by plants of the genus Taxus (yew trees) and are widely used as chemotherapy agents.[4]
Other
- Dodonaea petiolaris yields the diterpene ent-3β-acetoxy-15,16-epoxylabda-8(17),13(16),14-trien-18-oic acid (C22H28O6) or its enantiomer.[5]
- Salvia divinorum yields Salvinorin A, a psychotropic drug
References
- Eberhard Breitmaier (2006). "Diterpenes". Terpenes: Flavors, Fragrances, Pharmaca, Pheromones. pp. 52–81. doi:10.1002/9783527609949.ch4. ISBN 978-3-527-60994-9.
- Davis, Edward M.; Croteau, Rodney (2000). "Cyclization Enzymes in the Biosynthesis of Monoterpenes, Sesquiterpenes, and Diterpenes". Topics in Current Chemistry. 209: 53–95. doi:10.1007/3-540-48146-X_2. ISBN 978-3-540-66573-1.
- Pattanaik B, Lindberg P (January 2015). "Terpenoids and their biosynthesis in cyanobacteria". Life. 5 (1): 269–93. doi:10.3390/life5010269. PMC 4390852. PMID 25615610.
- Rowinsky, MD, Eric K. (February 1997). "The Development and Clinical Utility of the Taxane Class of Antimicrotubule Chemotherapy Agents". Annual Review of Medicine. 48 (1): 353–374. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.48.1.353. PMID 9046968.
- Jefferies, P. R.; Payne, T. G.; Raston, C. L.; White, A. H. (1981). "The chemistry of Dodonaea spp. VIII. Isolation and crystal structure of a diterpene acid from Dodonaea petiolaris". Australian Journal of Chemistry. 34 (5): 1001–1007. doi:10.1071/CH9811001.