Dithiobutylamine
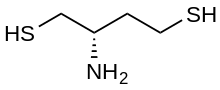
Dithiobutylamine (DTBA) is a reducing agent intended as an alternative for DTT in biochemical uses. It was designed to be easily synthesized in non-racemic form, to have a lower pKa (allowing more effective reduction at neutral pH), and to have a low disulfide E°′ reduction potential.[1] It was rationally designed & reported in 2012.[1] It is commercially available.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(S)-2-aminobutane-1,4-dithiol | |
| Other names
DTBA | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11NS2 | |
| Molar mass | 137.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid[1] |
| Odor | Nearly odorless[1] |
| Soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
- Dithiothreitol (DTT)
- 2-Mercaptoethanol (BME)
- TCEP
References
- Lukesh, John C.; Palte, Michael J.; Raines, Ronald T. (2012-02-21). "A Potent, Versatile Disulfide-Reducing Agent from Aspartic Acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society. American Chemical Society (ACS). 134 (9): 4057–4059. doi:10.1021/ja211931f. ISSN 0002-7863. PMC 3353773. PMID 22353145.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.