Trammel of Archimedes
A trammel of Archimedes is a mechanism that generates the shape of an ellipse.[1] It consists of two shuttles which are confined ("trammeled") to perpendicular channels or rails and a rod which is attached to the shuttles by pivots at fixed positions along the rod.

As the shuttles move back and forth, each along its channel, all points on the rod move in elliptical paths. The motion of the rod is termed elliptical motion. The semi-axes a and b of the ellipses have lengths equal to the distances from the point on the rod to each of the two pivots.
The straight lines described by the pivots are special cases of an ellipse, where the length of one axis is twice the distance between the pivots and that of the other is zero. All points on a circle with a diameter defined by the two pivots reciprocate in such straight lines. This circle corresponds to the smaller circle in a Tusi couple.
The point midway between the pivots orbits in a circle around the point where the channels cross. This circle is also a special case of an ellipse. Here the axes are of equal length. The diameter of the circle is equal to the distance between the pivots. The direction of travel around the orbit is opposite to the sense of rotation of the trammel. Thus, if a crank centred on the crossing point of the channels is used to engage the trammel at the midway point to drive it, the rotation of the crankpin and the trammel are equal and opposite, which in practical applications results in extra friction and accelerated wear. This is compounded by high forces owing to the short throw of the crank of only 1/4 the travel of the pivots.

Wooden versions of the trammel of Archimedes have been produced as devices to draw or cut ellipses, known as ellipsographs. Versions are also made as toys or novelty items (sold under the name of Kentucky do-nothings, nothing grinders, do nothing machines, smoke grinders, or bullshit grinders). In these toys the drafting instrument is replaced by a crank handle, and the position of the sliding shuttles is usually fixed.
Mathematics
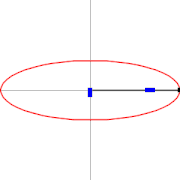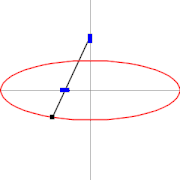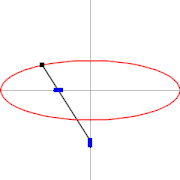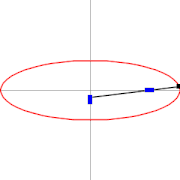 Trammel of Archimedes as ellipsograph
Trammel of Archimedes as ellipsograph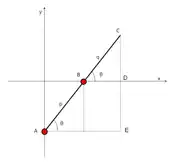 Diagram
Diagram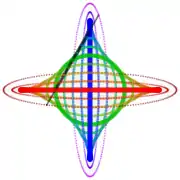 Loci of some points along and beyond a trammel of Archimedes, the green circle being the loci of its midpoint – in the SVG file, move the pointer over the diagram to move the trammel
Loci of some points along and beyond a trammel of Archimedes, the green circle being the loci of its midpoint – in the SVG file, move the pointer over the diagram to move the trammel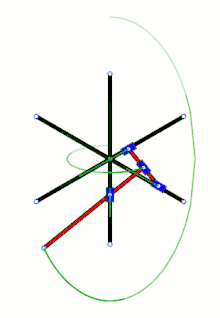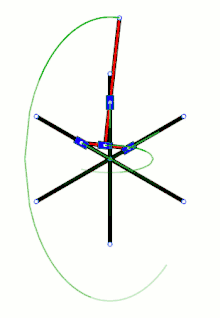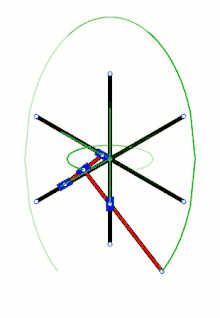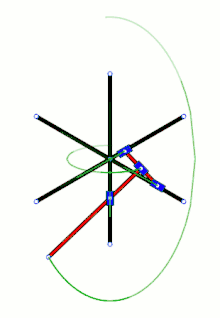 Trammel of Archimedes with three sliders
Trammel of Archimedes with three sliders
Let C be the outer end of the rod, and A, B be the pivots of the sliders. Let AB and BC be the distances from A to B and B to C, respectively. Let us assume that sliders A and B move along the y and x coordinate axes, respectively. When the rod makes an angle θ with the x-axis, the coordinates of point C are given by
These are in the form of the standard parametric equations for an ellipse in canonical position. The further equation
is immediate as well.
The trammel of Archimedes is an example of a four-bar linkage with two sliders and two pivots, and is special case of the more general oblique trammel. The axes constraining the pivots do not have to be perpendicular and the points A, B and C can form a triangle. The resulting locus of C is still an ellipse.[2]
Ellipsographs


An ellipsograph is a trammel of Archimedes intended to draw, cut, or machine ellipses, e.g. in wood or other sheet materials. An ellipsograph has the appropriate instrument (pencil, knife, router, etc.) attached to the rod. Usually the distances a and b are adjustable, so that the size and shape of the ellipse can be varied.
The history of such ellipsographs is not certain, but they are believed to date back to Proclus and perhaps even to the time of Archimedes.[2]
See also
Notes
- Schwartzman, Steven (1996). The Words of Mathematics. The Mathematical Association of America. ISBN 0-88385-511-9. (restricted online copy, p. 223, at Google Books)
- Wetzel, John E. (February 2010). "An Ancient Elliptic Locus". American Mathematical Monthly. 117 (2): 161–167. doi:10.4169/000298910x476068. JSTOR 10. S2CID 117701083.
References
- J. W. Downs: Practical Conic Sections: The Geometric Properties of Ellipses, Parabolas and Hyperbolas. Courier Dover 2003, ISBN 978-0-486-42876-5, pp. 4–5 (restricted online copy, p. 4, at Google Books)
- I. I. Artobolevskii Mechanisms for the Generation of Plane Curves. Pergamon Press 1964, ISBN 978-1483120003.
External links
- Video of various trammel designs in action
- Cutting ellipses in wood
- Photo of a Kentucky Do-Nothing
- Instructions on how to build a Kentucky Do-Nothing
- Video of a Do-Nothing made from Lego bricks
- "Wonky Trammel of Archimedes" An exploration of a generalized trammel.
- US-Patent 4306598 for ellipse cutting guide allowing small ellipses
- Secrets of the Nothing Grinder YouTube video by Mathologer